Article contents
Reduced-temperature solution-processed transparent oxide low-voltage-operable field-effect transistors
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 December 2015
Abstract
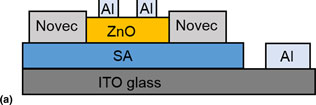
Metal oxide-based transistors can be fabricated by low-cost, large-area solution processing methods, but involve a trade-off between low processing temperature, facile charge transport and high-capacitance/low-voltage transistor gates. We achieve these simultaneously by fabricating zinc oxide and sodium-incorporated alumina (SA) thin films with temperature not exceeding 200 to 250 °C using aqueous and combustion precursors, respectively. X-ray reflectivity shows a compositionally distinct SA boundary layer forming near the substrate and that a portion of the SA is chemically removed during the subsequent semiconductor deposition. Improved etch resistance and reduced dielectric leakage was obtained when (3-glycidoxypropyl) trimethoxysilane was included in the SA precursor.
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2015
References
- 1
- Cited by




