Article contents
Anomalous characteristics of pore formation in Graphene induced by Si-nanoparticle bombardment
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 November 2017
Abstract
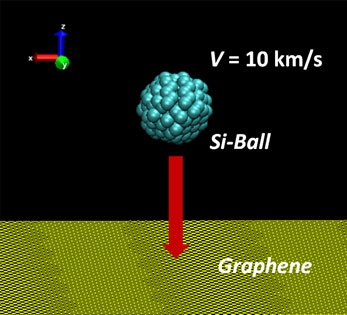
Graphene nanopores are utilized in various notable applications such as water desalination, molecular separation, and DNA sequencing. However, the creation of stable nanopores is still challenging due to the self-healing nature of graphene. In this study, using molecular dynamics simulations we explore the drilling of nanopores through graphene by bombardment with Si-nanoparticles. This enables the Si-passivation along the nanopore rim, which is known as an efficient way to stabilize graphene nanopores. The interplay between graphene and projectile causes the anomalous behaviors such as local maxima depending on particle size. The observations are thoroughly analyzed with interaction energy and shape changes.
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2017
References
- 1
- Cited by





