Article contents
Doping of TiO2 nanopowders with vanadium for the reduction of its band gap reaching the visible light spectrum region
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 03 June 2014
Abstract
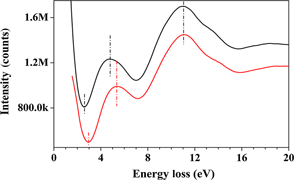
Titanium oxide (TiO2) nanoparticles (NPs) were doped with vanadium using a novel, facile, and inexpensive method. The TiO2 NPs were dispersed in a vanadyl oxalate solution prepared by dissolving vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) in oxalic acid. A short heat treatment at 400 °C applied to the dried mixture resulted in the doping of TiO2 with a net measured decrease of its band gap by about 0.5 eV, making this important semiconductor material usable in the visible light spectrum.
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2014
References
- 3
- Cited by




