No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
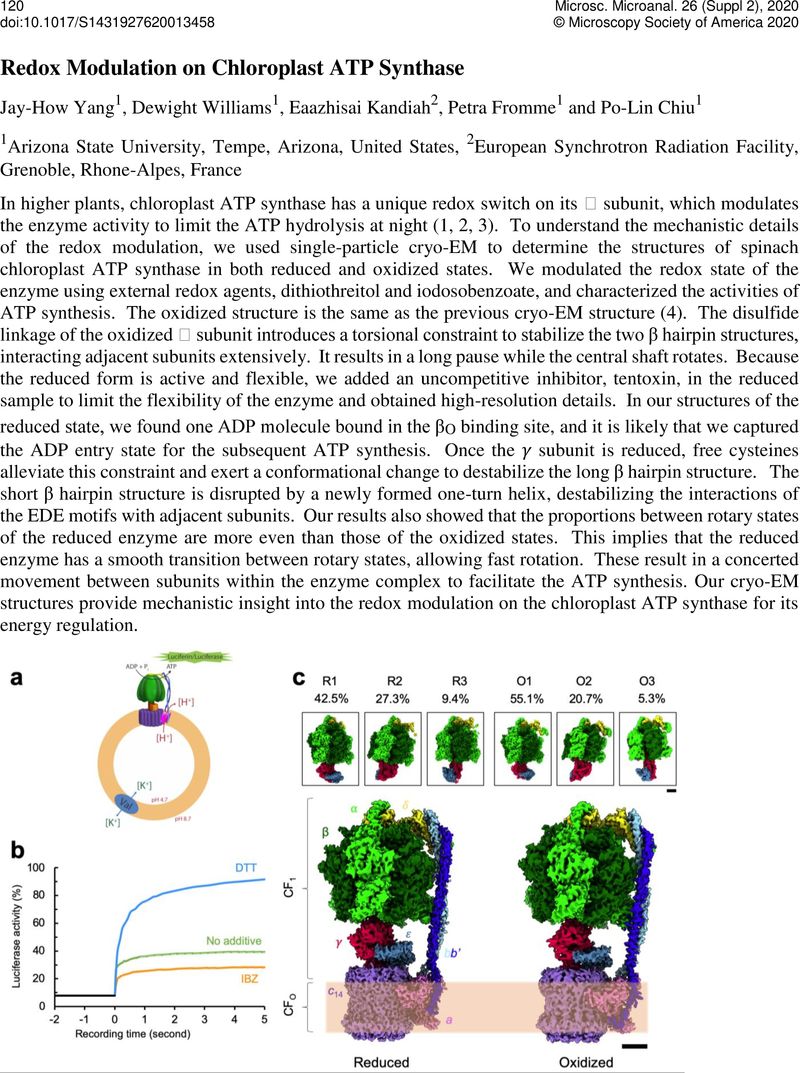
Redox Modulation on Chloroplast ATP Synthase
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 July 2020
Abstract
- Type
- 3D Structures: From Macromolecular Assemblies to Whole Cells (3DEM FIG)
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Microscopy Society of America 2020





