Article contents
A Novel Monochromator with Offset Cylindrical Lenses and Its Application to a Low-Voltage Scanning Electron Microscope
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 February 2022
Abstract
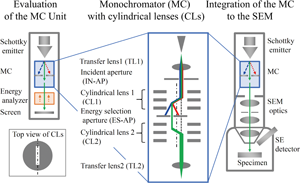
Low-voltage scanning electron microscopes (LV-SEMs) are widely used in nanoscience. However, image resolution for SEMs is restricted by chromatic aberration due to energy spread of the electron beam at low acceleration voltage. This study introduces a new monochromator (MC) with offset cylindrical lenses (CLs) as one solution for LV-SEMs. The MC optics, with highly excited CLs in offset layouts, has advantageous high performance and simple experimental setup, making it suitable for field emission LV-SEMs. In a preliminary evaluation, our MC reduced the energy spread from 770 to 67 meV. The MC was integrated into a commercial SEM equipped with an out-lens (a conventional objective lens without immersion magnetic or retarding electric fields) and an Everhart–Thornley detector. Comparing SEM images under two conditions with the MC turned on or off, the spatial resolution was improved by 58% at 0.5 and 1 keV. The filtering effect of the MC decreased the probe current with a ratio (i.e., transmittance) of 5.7%, which was consistent with estimations based on measured energy spreads. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on an effective MC with higher-energy resolution than 100 meV and the results offer encouraging prospects for LV-SEM technology.
Keywords
- Type
- Software and Instrumentation
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2022. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of the Microscopy Society of America
References
- 3
- Cited by





