Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Abedi-Varaki, Mehdi
2017.
The effect of the wiggler magnetic field strength on the self-focusing of an intense laser pulse propagating through a magnetized non-Maxwellian plasma.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 24,
Issue. 12,
Abedi-Varaki, M.
2018.
Enhanced THz radiation generation by photo-mixing of tophat lasers in rippled density plasma with a planar magnetostatic wiggler and s-parameter.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 25,
Issue. 2,
Abedi-Varaki, Mehdi
and
Jafari, Saed
2018.
The effects of helical magnetostatic wiggler on the modulation instability of a laser pulse propagating through a hot magnetoplasma.
Optik,
Vol. 158,
Issue. ,
p.
1240.
Abedi-Varaki, Mehdi
and
Jafari, Saed
2018.
Enhanced THz radiation from beating of two Cosh–Gaussian laser beams in a wiggler-assisted collisional magnetized plasma.
Journal of the Optical Society of America B,
Vol. 35,
Issue. 5,
p.
1165.
Abedi-Varaki, Mehdi
2018.
Electron acceleration by a circularly polarized electromagnetic wave publishing in plasma with a periodic magnetic field and an axial guide magnetic field.
Modern Physics Letters B,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 20,
p.
1850225.
Abedi‐Varaki, Mehdi
and
Panahi, Nasser
2019.
Non‐linear absorption of an intense laser pulse propagating in wiggler‐assisted underdense collisional plasma.
Contributions to Plasma Physics,
Vol. 59,
Issue. 9,
Abedi-Varaki, Mehdi
2019.
Electron acceleration of a surface wave propagating in wiggler-assisted plasma.
Modern Physics Letters B,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 23,
p.
1950267.
Abedi-Varaki, Mehdi
2020.
Effect of obliquely external magnetic field on the intense laser pulse propagating in plasma medium.
International Journal of Modern Physics B,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 07,
p.
2050044.
Chukkol, Yusuf Buba
and
Muminov, Mukhiddin
2020.
Shock-wave propagation in an isothermal slightly-compressible bubbly viscoelastic fluid flow.
Modern Physics Letters B,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 03,
p.
2050042.
Daraei, Mohammad Esmaeil
and
Abedi‐Varaki, Mehdi
2022.
Influence of non‐uniform magnetic field on relativistic q‐Gaussian laser pulses propagating in magnetized plasmas.
Contributions to Plasma Physics,
Vol. 62,
Issue. 8,
Abedi-Varaki, Mehdi
and
Kant, Niti
2022.
Magnetic field-assisted wakefield generation and electron acceleration by Gaussian and super-Gaussian laser pulses in plasma.
Modern Physics Letters B,
Vol. 36,
Issue. 07,
Tian, Kaijing
Xia, Xiongping
and
Gupta, Devki Nandan
2022.
Self-focusing/Defocusing of Hermite-Sinh-Gaussian Laser Beam in
Underdense Inhomogeneous Plasmas.
Laser and Particle Beams,
Vol. 2022,
Issue. ,
Abedi-Varaki, M.
and
Daraei, M.E.
2023.
Impact of wiggler magnetic field on wakefield generation and electron acceleration by Gaussian, super-Gaussian and Bessel–Gaussian laser pulses propagating in collisionless plasma.
Journal of Plasma Physics,
Vol. 89,
Issue. 1,
Abedi-Varaki, Mehdi
2023.
Relativistic laser third-harmonic generation from magnetized plasmas under a tapered magnetostatic wiggler.
Physics of Plasmas,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 8,
Abedi-Varaki, Mehdi
2023.
Generation of THz radiation by wakefield under a wiggler magnetic field: An analytical study.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment,
Vol. 1048,
Issue. ,
p.
168010.
Abedi-Varaki, Mehdi
2023.
The laser–plasma interaction: A bibliometric study.
International Journal of Modern Physics B,
Vol. 37,
Issue. 06,
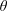 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$. Inversely, in left-hand polarization, increase of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$. Inversely, in left-hand polarization, increase of 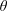 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$ in an oblique magnetic field leads to enhancement of the spot size and reduction self-focusing. Besides, in the plasma density profile, self-focusing of the laser pulse improves in comparison with no oblique magnetic field. Also it is shown that plasma temperature has a key role in the laser spot size, normalized laser output power and the variation of plasma density.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$ in an oblique magnetic field leads to enhancement of the spot size and reduction self-focusing. Besides, in the plasma density profile, self-focusing of the laser pulse improves in comparison with no oblique magnetic field. Also it is shown that plasma temperature has a key role in the laser spot size, normalized laser output power and the variation of plasma density.



