No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Low-temperature fabrication of nanocrystalline silicon thin films on mechanically flexible substrates by vacuum arc discharge
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 April 2011
Abstract
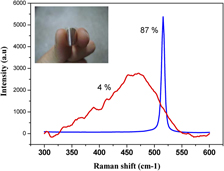
Nanocrystalline silicon thin films were fabricated using a vacuum arc discharge technique. These thin films can be deposited on plastic substrates effectively when cooled by a cryogenic substrate holder. We used single crystal silicon wafers as both the electrodes to ignite the vacuum arc and the silicon ion source to deposit thin films. This resulted in nanocrystalline silicon clusters embedded in the amorphous silicon matrix. This thin film has highly crystalline volume (≈87%), which enhanced the absorption in wide range of wavelengths. Without ion implantation, the in situ doping of p- or n-type thin films can also be achieved. This thin film deposition process has its potential for fabricating thin film transistors and photovoltaic cells on plastic substrates at fairly low production costs.
Keywords
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2011




