Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Cheng, Cheng
Li, Weipeng
Lozano-Durán, Adrián
and
Liu, Hong
2020.
On the structure of streamwise wall-shear stress fluctuations in turbulent channel flows.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 903,
Issue. ,
Xie, Jin-Han
de Silva, Charitha
Baidya, Rio
Yang, Xiang IA
and
Hu, Ruifeng
2021.
Third-order structure function in the logarithmic layer of boundary-layer turbulence.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 7,
Chen, Jianqiang
Dong, Siwei
Chen, Xi
Yuan, Xianxu
and
Xu, Guoliang
2021.
Stationary cross-flow breakdown in a high-speed swept-wing boundary layer.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 2,
Arosemena, Arturo A.
Andersson, Ronnie
Andersson, Helge I.
and
Solsvik, Jannike
2021.
Effects of shear-thinning rheology on near-wall turbulent structures.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 925,
Issue. ,
Frihat, Mohamed
Podvin, Bérengère
Mathelin, Lionel
Fraigneau, Yann
and
Yvon, François
2021.
Coherent structure identification in turbulent channel flow using latent Dirichlet allocation.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 920,
Issue. ,
Wang, Long-Wei
Pan, Chong
and
Wang, Jin-Jun
2022.
Wall-attached and wall-detached eddies in proper orthogonal decomposition modes of a turbulent channel flow.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 9,
Dong, Siwei
Tong, Fulin
Yu, Ming
Chen, Jianqiang
Yuan, Xianxu
and
Wang, Qian
2022.
Positive and negative pairs of fluctuating wall shear stress and heat flux in supersonic turbulent boundary layers.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 8,
Karban, U.
Martini, E.
Cavalieri, A.V.G.
Lesshafft, L.
and
Jordan, P.
2022.
Self-similar mechanisms in wall turbulence studied using resolvent analysis.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 939,
Issue. ,
Cheng, Cheng
and
Fu, Lin
2022.
Large-scale motions and self-similar structures in compressible turbulent channel flows.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 7,
Issue. 11,
Wang, Longwei
Pan, Chong
Wang, Jinjun
and
Gao, Qi
2022.
Statistical signatures of component wall-attached eddies in proper orthogonal decomposition modes of a turbulent boundary layer.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 944,
Issue. ,
Xia, Yuxian
Qiu, Xiang
and
Qian, Yuehong
2022.
Influence of turbulent structure on the heat transfer of Rayleigh–Bénard convection with triangular roughness element.
Journal of Turbulence,
Vol. 23,
Issue. 11-12,
p.
549.
Cheng, Cheng
Shyy, Wei
and
Fu, Lin
2022.
Streamwise inclination angle of wall-attached eddies in turbulent channel flows.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 946,
Issue. ,
Wu, Gen
Fang, Le
and
Zhang, Jin
2022.
Numerical investigation and parametric analysis of an attached eddy model applied to inlet condition.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 11,
Heisel, Michael
de Silva, Charitha M.
Katul, Gabriel G.
and
Chamecki, Marcelo
2022.
Self-similar geometries within the inertial subrange of scales in boundary layer turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 942,
Issue. ,
Yuan, Xianxu
Tong, Fulin
Li, Weipeng
Chen, Jianqiang
and
Dong, Siwei
2022.
Wall-attached temperature structures in supersonic turbulent boundary layers.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 11,
Li, Fangbo
Pei, Binbin
and
Bai, Bofeng
2022.
Scaling laws of statistics of wall-bounded turbulence at supercritical pressure: Evaluation and mechanism.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 8,
Hu, Ruifeng
Zheng, Xiaojing
and
Dong, Siwei
2022.
Extracting discrete hierarchies of Townsend's wall-attached eddies.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 6,
Cheng, Cheng
and
Fu, Lin
2023.
A scale-based study of the Reynolds number scaling for the near-wall streamwise turbulence intensity in wall turbulence.
International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow,
Vol. 101,
Issue. ,
p.
109136.
Yin, Yanxin
Wu, Yongjun
Wang, Run
Ren, Chong
Qu, Qiang
Zhang, Qingqing
and
Liu, Jin
2023.
Positive and negative wall-pressure fluctuations beneath a supersonic turbulent boundary layer.
Acta Mechanica Sinica,
Vol. 39,
Issue. 1,
Cheng, Cheng
and
Fu, Lin
2023.
Linear-model-based study of the coupling between velocity and temperature fields in compressible turbulent channel flows.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 964,
Issue. ,
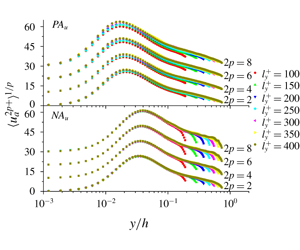
 $Re_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}}=186$, 358, 547 and 934). The statistical properties of the structures, such as their geometric self-similarity, population density and statistical moments, are investigated and compared with the predictions of the attached-eddy model. Particular attention is paid to the asymmetries between high- and low-speed wall-attached streaky structures, and we show that the former are a closer representation of the wall-attached eddies. This observation is ascribed to the differences between the sweep and ejection events associated with the streaks. We also examine the Reynolds-number effects on the statistical properties of the structures, and find that the signature of attached eddies can be observed within the Reynolds-number range under scrutiny. Our approach paves the way to cost-efficient model development and flow prediction using computationally more affordable simulations at low Reynolds numbers.
$Re_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}}=186$, 358, 547 and 934). The statistical properties of the structures, such as their geometric self-similarity, population density and statistical moments, are investigated and compared with the predictions of the attached-eddy model. Particular attention is paid to the asymmetries between high- and low-speed wall-attached streaky structures, and we show that the former are a closer representation of the wall-attached eddies. This observation is ascribed to the differences between the sweep and ejection events associated with the streaks. We also examine the Reynolds-number effects on the statistical properties of the structures, and find that the signature of attached eddies can be observed within the Reynolds-number range under scrutiny. Our approach paves the way to cost-efficient model development and flow prediction using computationally more affordable simulations at low Reynolds numbers.



