Article contents
Modulation-resonance mechanism for surface waves in a two-layer fluid system
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 July 2019
Abstract
We propose a Boussinesq-type model to study the surface/interfacial wave manifestation of an underlying, slowly varying, long-wavelength baroclinic flow in a two-layer, density-stratified system. The results of our model show numerically that, under strong nonlinearity, surface waves, with their typical wavenumber being the resonant 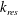 $k_{res}$, can be generated locally at the leading edge of the underlying, slowly varying, long-wavelength baroclinic flow. Here, the resonant
$k_{res}$, can be generated locally at the leading edge of the underlying, slowly varying, long-wavelength baroclinic flow. Here, the resonant 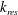 $k_{res}$ satisfies the class 3 triad resonance condition among two short-mode waves and one long-mode wave in which all waves propagate in the same direction. Moreover, when the slope of the baroclinic flow is sufficiently small, only one spatially localized large-amplitude surface wave packet can be generated at the leading edge. This localized surface wave packet becomes high in amplitude and large in group velocity after the interaction with its surrounding waves. These results are qualitatively consistent with various experimental observations including resonant surface waves at the leading edge of an internal wave. Subsequently, we propose a mechanism, referred to as the modulation-resonance mechanism, underlying these surface phenomena, based on our numerical simulations. The proposed modulation-resonance mechanism combines the linear modulation, ray-based, theory for the spatiotemporal asymmetric behaviour of surface waves and the nonlinear class 3 triad resonance theory for the energy focusing of surface waves around the resonant wavenumber
$k_{res}$ satisfies the class 3 triad resonance condition among two short-mode waves and one long-mode wave in which all waves propagate in the same direction. Moreover, when the slope of the baroclinic flow is sufficiently small, only one spatially localized large-amplitude surface wave packet can be generated at the leading edge. This localized surface wave packet becomes high in amplitude and large in group velocity after the interaction with its surrounding waves. These results are qualitatively consistent with various experimental observations including resonant surface waves at the leading edge of an internal wave. Subsequently, we propose a mechanism, referred to as the modulation-resonance mechanism, underlying these surface phenomena, based on our numerical simulations. The proposed modulation-resonance mechanism combines the linear modulation, ray-based, theory for the spatiotemporal asymmetric behaviour of surface waves and the nonlinear class 3 triad resonance theory for the energy focusing of surface waves around the resonant wavenumber  $k_{res}$ in Fourier space.
$k_{res}$ in Fourier space.
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2019 Cambridge University Press
References
- 8
- Cited by




