Article contents
Dynamic simulation of a coated microbubble in an unbounded flow: response to a step change in pressure
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 June 2017
Abstract
A numerical method is developed to study the dynamic behaviour of an encapsulated bubble when the viscous forces of the surrounding liquid are accounted for. The continuity and Navier–Stokes equations are solved for the liquid, whereas the coating is described as a viscoelastic shell with bending resistance. The Galerkin Finite Element Methodology is employed for the spatial discretization of the flow domain surrounding the bubble, with the standard staggered grid arrangement that uses biquadratic and bilinear Lagrangian basis functions for the velocity and pressure in the liquid, respectively, coupled with a superparametric scheme with 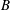 $B$-cubic splines as basis functions pertaining to the location of the interface. The spine method and the elliptic mesh generation technique are used for updating the mesh points in the interior of the flow domain as the shape of the interface evolves with time, with the latter being distinctly superior in capturing severely distorted shapes. The stabilizing effect of the liquid viscosity is demonstrated, as it alters the amplitude of the disturbance for which a bubble deforms and/or collapses. For a step change in the far-field pressure the dynamic evolution of the microbubble is captured until a static equilibrium is achieved. Static shapes that are significantly compressed are captured in the post-buckling regime, leading to symmetric or asymmetric shapes, depending on the relative dilatation to bending stiffness ratio. As the external overpressure increases, shapes corresponding to all the solution families that were captured evolve to exhibit contact as the two poles approach each other. Shell viscosity prevents jet formation by relaxing compressive stresses and bending moments around the indentation generated at the poles due to shell buckling. This behaviour is conjectured to be the inception process leading to static shapes with contact regions.
$B$-cubic splines as basis functions pertaining to the location of the interface. The spine method and the elliptic mesh generation technique are used for updating the mesh points in the interior of the flow domain as the shape of the interface evolves with time, with the latter being distinctly superior in capturing severely distorted shapes. The stabilizing effect of the liquid viscosity is demonstrated, as it alters the amplitude of the disturbance for which a bubble deforms and/or collapses. For a step change in the far-field pressure the dynamic evolution of the microbubble is captured until a static equilibrium is achieved. Static shapes that are significantly compressed are captured in the post-buckling regime, leading to symmetric or asymmetric shapes, depending on the relative dilatation to bending stiffness ratio. As the external overpressure increases, shapes corresponding to all the solution families that were captured evolve to exhibit contact as the two poles approach each other. Shell viscosity prevents jet formation by relaxing compressive stresses and bending moments around the indentation generated at the poles due to shell buckling. This behaviour is conjectured to be the inception process leading to static shapes with contact regions.
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2017 Cambridge University Press
References
- 9
- Cited by





