Article contents
Analytic model of a resistive magnetohydrodynamic shock without Hall effect
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 March 2018
Abstract
An analytic model of a stationary hypersonic magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) shock with an externally applied magnetic field is proposed. Basically, original jump conditions at a plane oblique shock, analogous to the Rankine–Hugoniot formulae, with a moderately resistive air plasma downstream are derived. Viscous, thermal and Hall effects are neglected, but the plasma dissociation behind the shock causing a jump of isentropic exponent is also a major input of the model. Then, a shock-fitting procedure with ambient atmospheric conditions is worked out by the coupling of these MHD jumps with thermodynamic correlations and an electric conductivity model. For an application to atmospheric entry problems, the flow behind an axisymmetric blunt-body shock is modelled with a stream function satisfying these MHD jump conditions as boundary conditions. An important feature put into evidence is a similarity rule involving the hypersonic parameter 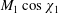 $M_{1}\cos \unicode[STIX]{x1D712}_{1}$, which shows an aerodynamic correspondence between the upstream Mach number
$M_{1}\cos \unicode[STIX]{x1D712}_{1}$, which shows an aerodynamic correspondence between the upstream Mach number 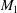 $M_{1}$ and the velocity angle
$M_{1}$ and the velocity angle  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D712}_{1}$. It also emerges that curvature effects become important past
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D712}_{1}$. It also emerges that curvature effects become important past 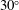 $30^{\circ }$ and the assumption of a spherical shock also becomes untenable past
$30^{\circ }$ and the assumption of a spherical shock also becomes untenable past 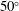 $50^{\circ }$; therefore, we limit the model of shock thickness used in the MHD fitting to
$50^{\circ }$; therefore, we limit the model of shock thickness used in the MHD fitting to 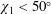 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D712}_{1}<50^{\circ }$.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D712}_{1}<50^{\circ }$.
JFM classification
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2018 Cambridge University Press
References
- 5
- Cited by





