No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
A generalisation of Dirichlet's multiple integral
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 31 October 2008
Extract
The well-known multiple integral
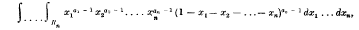
where Rn is the region defined by x1 ≥ 0, x2 ≥ 0, …., xn ≥ 0, x1 + x2 + …. + xn ≤ 1, and where a0, a1, …, an are positive constants, can be evaluated either in the classical way using the Dirichlet transformation or by the use of the Laplace transform. I. J. Good has considered a more general integral and has proved the following result by induction:—
If f1(t), f2(t), …, fn(t) are Lebesgue measurable for 0 ≤ t ≤ 1, m1, m2, …., mn, mn+1 (= 0) are real numbers, Mr = m1 + m2 + … + mr, x1, x2, …, xn are non-negative variables and Xr = x1 + x2 + … + xr, then
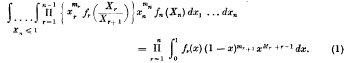
It does not seem to be possible to establish this relation by employing the Laplace transform, but we show below that it can be obtained using the Mellin transform.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Edinburgh Mathematical Society 1956




