Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Castermant, J.
Mendonça, C.A.
Revil, A.
Trolard, F.
Bourrié, G.
and
Linde, N.
2008.
Redox potential distribution inferred from self‐potential measurements associated with the corrosion of a burden metallic body.
Geophysical Prospecting,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 2,
p.
269.
Trolard, Fabienne
and
Bourrié, Guilhem
2008.
Vol. 99,
Issue. ,
p.
227.
Larese-Casanova, Philip
and
Scherer, Michelle M.
2008.
Abiotic Transformation of Hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) by Green Rusts.
Environmental Science & Technology,
Vol. 42,
Issue. 11,
p.
3975.
Chukanov, N. V.
Pekov, I. V.
Levitskaya, L. A.
and
Zadov, A. E.
2009.
Droninoite, Ni3Fe3+Cl(OH)8 · 2H2O, a new hydrotalcite-group mineral species from the weathered Dronino meteorite.
Geology of Ore Deposits,
Vol. 51,
Issue. 8,
p.
767.
Ona-Nguema, Georges
Morin, Guillaume
Wang, Yuheng
Menguy, Nicolas
Juillot, Farid
Olivi, Luca
Aquilanti, Giuliana
Abdelmoula, Mustapha
Ruby, Christian
Bargar, John R.
Guyot, François
Calas, Georges
and
Brown, Gordon E.
2009.
Arsenite sequestration at the surface of nano-Fe(OH)2, ferrous-carbonate hydroxide, and green-rust after bioreduction of arsenic-sorbed lepidocrocite by Shewanella putrefaciens.
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,
Vol. 73,
Issue. 5,
p.
1359.
Barchiche, Ch.
Deslouis, C.
Gil, O.
Joiret, S.
Refait, Ph.
and
Tribollet, B.
2009.
Role of sulphate ions on the formation of calcareous deposits on steel in artificial seawater; the formation of Green Rust compounds during cathodic protection.
Electrochimica Acta,
Vol. 54,
Issue. 13,
p.
3580.
Davesne, E.
Dideriksen, K.
Christiansen, B.C.
Sonne, M.
Ayala-Luis, K.B.
Koch, C. Bender
Hansen, H.C.B.
and
Stipp, S.L.S.
2010.
Free energy of formation for green rust sodium sulphate (NaFeII6FeIII3(OH)18(SO4)2(s)).
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,
Vol. 74,
Issue. 22,
p.
6451.
Singh, Balwant
Gräfe, Markus
Kaur, Navdeep
and
Liese, Andrea
2010.
Synchrotron-Based Techniques in Soils and Sediments.
Vol. 34,
Issue. ,
p.
199.
Cho, Dong-Wan
Chon, Chul-Min
Jeon, Byong-Hun
Kim, Yongje
Khan, Moonis Ali
and
Song, Hocheol
2010.
The role of clay minerals in the reduction of nitrate in groundwater by zero-valent iron.
Chemosphere,
Vol. 81,
Issue. 5,
p.
611.
Krivovichev, Sergey V.
Yakovenchuk, Victor N.
and
Zhitova, Elena S.
2011.
Minerals as Advanced Materials II.
p.
87.
Christiansen, B. C.
Dideriksen, K.
Skovbjerg, L. L.
Nedel, S.
and
Stipp, S. L. S.
2011.
Letter to the Editor on Fougerite.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 59,
Issue. 1,
p.
3.
Jorand, F.
Zegeye, A.
Ghanbaja, J.
and
Abdelmoula, M.
2011.
The formation of green rust induced by tropical river biofilm components.
Science of The Total Environment,
Vol. 409,
Issue. 13,
p.
2586.
Trolard, F.
and
Bourrié, G.
2011.
Reply to the Letter to the Editor by Christiansen, Dideriksen, Skovbjerg, Nedel, and Stipp: “On Fougerite”.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 59,
Issue. 1,
p.
10.
Witzke, T.
Torres-Dorante, L.
Bullerjahn, F.
and
Pöllmann, H.
2011.
Minerals as Advanced Materials II.
p.
131.
Huber, Claudia
Kraus, Florian
Hanzlik, Marianne
Eisenreich, Wolfgang
and
Wächtershäuser, Günter
2012.
Elements of Metabolic Evolution.
Chemistry – A European Journal,
Vol. 18,
Issue. 7,
p.
2063.
Mills, S. J.
Christy, A. G.
Génin, J.-M. R.
Kameda, T.
and
Colombo, F.
2012.
Nomenclature of the hydrotalcite supergroup: natural layered double hydroxides.
Mineralogical Magazine,
Vol. 76,
Issue. 5,
p.
1289.
Pantke, Claudia
Obst, Martin
Benzerara, Karim
Morin, Guillaume
Ona-Nguema, Georges
Dippon, Urs
and
Kappler, Andreas
2012.
Green Rust Formation during Fe(II) Oxidation by the Nitrate-Reducing Acidovorax sp. Strain BoFeN1.
Environmental Science & Technology,
Vol. 46,
Issue. 3,
p.
1439.
Curtius, Hilde
Kaiser, Gabriel
Rozov, Konstantin
Neumann, Andreas
Dardenne, Kathy
and
Bosbach, Dirk
2013.
Preparation and Characterization of Fe-, Co-, and Ni-Containing Mg-Al-Layered Double Hydroxides.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 61,
Issue. 5,
p.
424.
Newman, T. G.
Ghail, R. C.
and
Skipper, J. A.
2013.
Deoxygenated gas occurrences in the Lambeth Group of central London, UK.
Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology,
Vol. 46,
Issue. 2,
p.
167.
O’Loughlin, Edward J.
Boyanov, Maxim I.
Flynn, Theodore M.
Gorski, Christopher A.
Hofmann, Scott M.
McCormick, Michael L.
Scherer, Michelle M.
and
Kemner, Kenneth M.
2013.
Effects of Bound Phosphate on the Bioreduction of Lepidocrocite (γ-FeOOH) and Maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) and Formation of Secondary Minerals.
Environmental Science & Technology,
Vol. 47,
Issue. 16,
p.
9157.
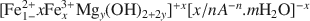 where A is the interlayer anion and n its valency, with 1/4 ≼ x/(1+y) ≼ 1/3 and m ≼ (1−x+y). The structure of green rusts and parent minerals can accommodate a variety of anions, such as OH−, Cl−, CO32−,SO42−${\rm{CO}}_3^{2 - },\;{\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$
where A is the interlayer anion and n its valency, with 1/4 ≼ x/(1+y) ≼ 1/3 and m ≼ (1−x+y). The structure of green rusts and parent minerals can accommodate a variety of anions, such as OH−, Cl−, CO32−,SO42−${\rm{CO}}_3^{2 - },\;{\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$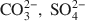 . The structure of the mineral was studied by Mössbauer, Raman and X-ray absorption spectroscopies (XAS) at the FeK edge. Mössbauer spectra of the mineral obtained at 78 K are best fitted with four doublets: D1 and D2 due to Fe2+ (isomer shift δ ≈ 1.27 and 1.25 mm s−1, quadrupole splitting ΔEQ ≈ 2.86 and 2.48 mm s−1, respectively) and D3 and D4 due to Fe3+ (δ ≈ 0.46 mm s−1, ΔEQ ≈ 0.48 and 0.97 mm s−1, respectively). Microprobe Raman spectra obtained with a laser at 514.53 nm show the characteristic bands of synthetic green rusts at 427 and 518 cm−1. X-ray absorption spectroscopy shows that Mg is present in the mineral in addition to Fe, that the space group is and the lattice parameter a ≈ 0.30–0.32 nm. The mineral forms by partial oxidation and hydrolysis of aqueous Fe2+, to give small crystals (400–500 nm) in the form of hexagonal plates. The mineral is unstable in air and transforms to lepidocrocite or goethite. The name is for the locality of the occurrence, a forested Gleysol near Fougères, Brittany, France. Its characteristic blue-green color (5BG6/1 in the Munsell system) has long been used as a universal criterion in soil classification to identify Gleysols. From a thermodynamic model of soil-solution equilibria, it was proposed that for the eponymous mineral, Fougères-fougerite, OH− may be the interlayer anion. In other environments, the interlayer anion may be different, and other varieties of fougerite may exist. Fougerite plays a key role in the pathways of formation of Fe oxides.
. The structure of the mineral was studied by Mössbauer, Raman and X-ray absorption spectroscopies (XAS) at the FeK edge. Mössbauer spectra of the mineral obtained at 78 K are best fitted with four doublets: D1 and D2 due to Fe2+ (isomer shift δ ≈ 1.27 and 1.25 mm s−1, quadrupole splitting ΔEQ ≈ 2.86 and 2.48 mm s−1, respectively) and D3 and D4 due to Fe3+ (δ ≈ 0.46 mm s−1, ΔEQ ≈ 0.48 and 0.97 mm s−1, respectively). Microprobe Raman spectra obtained with a laser at 514.53 nm show the characteristic bands of synthetic green rusts at 427 and 518 cm−1. X-ray absorption spectroscopy shows that Mg is present in the mineral in addition to Fe, that the space group is and the lattice parameter a ≈ 0.30–0.32 nm. The mineral forms by partial oxidation and hydrolysis of aqueous Fe2+, to give small crystals (400–500 nm) in the form of hexagonal plates. The mineral is unstable in air and transforms to lepidocrocite or goethite. The name is for the locality of the occurrence, a forested Gleysol near Fougères, Brittany, France. Its characteristic blue-green color (5BG6/1 in the Munsell system) has long been used as a universal criterion in soil classification to identify Gleysols. From a thermodynamic model of soil-solution equilibria, it was proposed that for the eponymous mineral, Fougères-fougerite, OH− may be the interlayer anion. In other environments, the interlayer anion may be different, and other varieties of fougerite may exist. Fougerite plays a key role in the pathways of formation of Fe oxides.



