Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Glorgetti, Glovanna
Monecke, Thomas
Kleeberg, Reinhard
and
Hannington, Mark D.
2006.
Low-Temperature Hydrothermal Alteration of Silicic Glass at the PACMANUS Hydrothermal Vent Field, Manus Basin: An XRD, SEM and AEM-TEM study.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 54,
Issue. 2,
p.
240.
Kaçmaz, H.
and
Köktürk, U.
2006.
Zeolites and Coexisting Authigenic Minerals in Miocene Tuffs of the Alaçatı (Çeşme) Area, Turkey.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 54,
Issue. 5,
p.
587.
Monecke, T.
Giorgetti, G.
Scholtysek, O.
Kleeberg, R.
Götze, J.
Hannington, M.D.
and
Petersen, S.
2007.
Textural and mineralogical changes associated with the incipient hydrothermal alteration of glassy dacite at the submarine PACMANUS hydrothermal system, eastern Manus Basin.
Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,
Vol. 160,
Issue. 1-2,
p.
23.
Hints, Rutt
Kirsimäe, Kalle
Somelar, Peeter
Kallaste, Toivo
and
Kiipli, Tarmo
2008.
Multiphase Silurian bentonites in the Baltic Palaeobasin.
Sedimentary Geology,
Vol. 209,
Issue. 1-4,
p.
69.
MUTTIK, Nele
KIRSIMÄE, Kalle
Somelar, Peeter
and
Osinski, Gordon R.
2008.
Post‐impact alteration of surficial suevites in Ries crater, Germany: Hydrothermal modification or weathering processes?.
Meteoritics & Planetary Science,
Vol. 43,
Issue. 11,
p.
1827.
Yuan, Hongji
and
Bish, David L.
2010.
Automated Fitting of X-Ray Powder Diffraction Patterns from Interstratified Phyllosilicates.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 58,
Issue. 6,
p.
727.
Yuan, Hongji
and
Bish, David L.
2010.
Newmod+, a New Version of the Newmod Program for Interpreting X-Ray Powder Diffraction Patterns from Interstratified Clay Minerals.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 58,
Issue. 3,
p.
318.
Plevová, E.
Vaculíková, L.
Kožušníková, A.
Daněk, T.
Pleva, M.
Ritz, M.
and
Simha Martynková, G.
2011.
Thermal study of sandstones from different Czech localities.
Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry,
Vol. 103,
Issue. 3,
p.
835.
McKeown, Nancy K.
Bishop, Janice L.
Cuadros, Javier
Hillier, Stephen
Amador, Elena
Makarewicz, Heather D.
Parente, Mario
and
Silver, Eli A.
2011.
Interpretation of Reflectance Spectra of Clay Mineral-Silica Mixtures: Implications for Martian Clay Mineralogy at Mawrth Vallis.
Clays and Clay Minerals,
Vol. 59,
Issue. 4,
p.
400.
Cuadros, J.
2012.
Clay crystal-chemical adaptability and transformation mechanisms.
Clay Minerals,
Vol. 47,
Issue. 2,
p.
147.
Cuadros, J.
Afsin, B.
Jadubansa, P.
Ardakani, M.
Ascaso, C.
and
Wierzchos, J.
2013.
Pathways of volcanic glass alteration in laboratory experiments through inorganic and microbially-mediated processes.
Clay Minerals,
Vol. 48,
Issue. 3,
p.
423.
Hong, Hanlie
Fang, Qian
Wang, Chaowen
Churchman, Gordon Jock
Zhao, Lulu
Gong, Nina
and
Yin, Ke
2017.
Clay mineralogy of altered tephra beds and facies correlation between the Permian-Triassic boundary stratigraphic sets, Guizhou, south China.
Applied Clay Science,
Vol. 143,
Issue. ,
p.
10.
Hong, Hanlie
Fang, Qian
Zhao, Lulu
Schoepfer, Shane
Wang, Chaowen
Gong, Nina
Li, Zhaohui
and
Chen, Zhong-Qiang
2017.
Weathering and alteration of volcanic ashes in various depositional settings during the Permian-Triassic transition in South China: Mineralogical, elemental and isotopic approaches.
Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology,
Vol. 486,
Issue. ,
p.
46.
Zhang, Yuxiang
Zeng, Zhigang
Qi, Haiyan
Yin, Xuebo
Li, He
Wang, Xiaoyuan
and
Chen, Shuai
2018.
Two-stage influences of hydrothermal fluids on pumice near the Iheya North hydrothermal field, Okinawa Trough.
Marine Georesources & Geotechnology,
Vol. 36,
Issue. 4,
p.
393.
Peretyazhko, T.S.
Niles, P.B.
Sutter, B.
Morris, R.V.
Agresti, D.G.
Le, L.
and
Ming, D.W.
2018.
Smectite formation in the presence of sulfuric acid: Implications for acidic smectite formation on early Mars.
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,
Vol. 220,
Issue. ,
p.
248.
Hong, Hanlie
Zhao, Lulu
Fang, Qian
Algeo, Thomas J.
Wang, Chaowen
Yu, Jianxin
Gong, Nina
Yin, Ke
and
Ji, Kaipeng
2019.
Volcanic sources and diagenetic alteration of Permian–Triassic boundary K-bentonites in Guizhou Province, South China.
Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology,
Vol. 519,
Issue. ,
p.
141.
Roháč, Jakub
Scaringi, Gianvito
Boháč, Jan
Kycl, Petr
and
Najser, Jan
2020.
Revisiting strength concepts and correlations with soil index properties: insights from the Dobkovičky landslide in Czech Republic.
Landslides,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 3,
p.
597.
Fontaine, François
Christidis, George E.
Yans, Johan
Hollanders, Sofie
Hoffman, Andreas
and
Fagel, Nathalie
2020.
Characterization and origin of two Fe-rich bentonites from Westerwald (Germany).
Applied Clay Science,
Vol. 187,
Issue. ,
p.
105444.
Sun, Ningliang
Zhong, Jianhua
Hao, Bing
Ge, Yuzhu
and
Swennen, Rudy
2020.
Sedimentological and diagenetic control on the reservoir quality of deep-lacustrine sedimentary gravity flow sand reservoirs of the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in Southern Ordos Basin, China.
Marine and Petroleum Geology,
Vol. 112,
Issue. ,
p.
104050.
Sun, Ningliang
Zhong, Jianhua
Ge, Yuzhu
and
van Loon, A.J. (Tom)
2022.
The Ordos Basin.
p.
421.
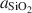 ) showed that some solution compositions are consistent and some are inconsistent with I-S formation. These results, combined with complementary electron microscopy analyses (de la Fuente et al., 2000a), are interpreted to be due to direct transformation of the glass into I-S in a process controlled by glass composition.
) showed that some solution compositions are consistent and some are inconsistent with I-S formation. These results, combined with complementary electron microscopy analyses (de la Fuente et al., 2000a), are interpreted to be due to direct transformation of the glass into I-S in a process controlled by glass composition.



