Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Tran, Damien
Haberkorn, Hansy
Soudant, Philippe
Ciret, Pierre
and
Massabuau, Jean-Charles
2010.
Behavioral responses of Crassostrea gigas exposed to the harmful algae Alexandrium minutum.
Aquaculture,
Vol. 298,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
338.
Mafra, Luiz L.
Bricelj, V. Monica
and
Fennel, Katja
2010.
Domoic acid uptake and elimination kinetics in oysters and mussels in relation to body size and anatomical distribution of toxin.
Aquatic Toxicology,
Vol. 100,
Issue. 1,
p.
17.
Navarro, Jorge M.
Aguila, Blanca L.
Machmar, Fabiola
Chaparro, Oscar R.
and
Contreras, Andrea M.
2011.
Dynamic of intoxication and detoxification in juveniles ofMytilus chilensis(Bivalvia: Mytilidae) exposed to paralytic shellfish toxins.
Aquatic Living Resources,
Vol. 24,
Issue. 1,
p.
93.
Haberkorn, Hansy
Tran, Damien
Massabuau, Jean-Charles
Ciret, Pierre
Savar, Véronique
and
Soudant, Philippe
2011.
Relationship between valve activity, microalgae concentration in the water and toxin accumulation in the digestive gland of the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas exposed to Alexandrium minutum.
Marine Pollution Bulletin,
Vol. 62,
Issue. 6,
p.
1191.
Guéguen, Marielle
Baron, Régis
Bardouil, Michèle
Truquet, Philippe
Haberkorn, Hansy
Lassus, Patrick
Barillé, Laurent
and
Amzil, Zouher
2011.
Modelling of paralytic shellfish toxin biotransformations in the course of Crassostrea gigas detoxification kinetics.
Ecological Modelling,
Vol. 222,
Issue. 18,
p.
3394.
Medhioub, Walid
Lassus, Patrick
Truquet, Philippe
Bardouil, Michèle
Amzil, Zouher
Sechet, Véronique
Sibat, Manoella
and
Soudant, Philippe
2012.
Spirolide uptake and detoxification by Crassostrea gigas exposed to the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii.
Aquaculture,
Vol. 358-359,
Issue. ,
p.
108.
Guéguen, Marielle
Baron, Régis
Bardouil, Michèle
Haberkorn, Hansy
Soudant, Philippe
Truquet, Philippe
and
Lassus, Patrick
2012.
Influence of Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg) sexual maturation stage and ploidy on uptake of paralytic phycotoxins.
Toxicon,
Vol. 60,
Issue. 1,
p.
40.
Rolland, Jean-Luc
Pelletier, Kevin
Masseret, Estelle
Rieuvilleneuve, Fabien
Savar, Veronique
Santini, Adrien
Amzil, Zouher
and
Laabir, Mohamed
2012.
Paralytic Toxins Accumulation and Tissue Expression of α-Amylase and Lipase Genes in the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas Fed with the Neurotoxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella.
Marine Drugs,
Vol. 10,
Issue. 11,
p.
2519.
Mat, Audrey M.
Haberkorn, Hansy
Bourdineaud, Jean-Paul
Massabuau, Jean-Charles
and
Tran, Damien
2013.
Genetic and genotoxic impacts in the oyster Crassostrea gigas exposed to the harmful alga Alexandrium minutum.
Aquatic Toxicology,
Vol. 140-141,
Issue. ,
p.
458.
Jiang, Tao
Xu, Yixiao
Li, Yang
Jiang, Tianjiu
Wu, Feng
and
Zhang, Fan
2014.
Seasonal dynamics of Alexandrium tamarense and occurrence of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in bivalves in Nanji Islands, East China Sea.
Marine and Freshwater Research,
Vol. 65,
Issue. 4,
p.
350.
Rolland, Jean-Luc
Medhioub, Walid
Vergnes, Agnes
Abi-khalil, Celina
Savar, Véronique
Abadie, Eric
Masseret, Estelle
Amzil, Zouher
and
Laabir, Mohamed
2014.
A Feedback Mechanism to Control Apoptosis Occurs in the Digestive Gland of the Oyster Crassostrea gigas Exposed to the Paralytic Shellfish Toxins Producer Alexandrium catenella.
Marine Drugs,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 9,
p.
5035.
Xu, Yan-Yan
Liang, Jin-Jin
Yang, Wei-Dong
Wang, Jie
Li, Hong-Ye
and
Liu, Jie-Sheng
2014.
Cloning and expression analysis of P-glycoprotein gene in Crassostrea ariakensis.
Aquaculture,
Vol. 418-419,
Issue. ,
p.
39.
Haure, J.
Hussenot, J.
Buzin, F.
Lassus, Patrick
Marcaillou, C.
Mondeguer, F.
Séchet, V.
Royer, F.
Amzil, Zouher
Cardinal, M.
Le Grel, L.
Massé, A.
Sabiri, N. E.
Castaing, J. B.
and
Jaouen, P.
2014.
Molluscan Shellfish Safety.
p.
25.
Kaga, Shinnosuke
Sato, Shigeru
Kaga, Yoshimasa
Naiki, Kimiaki
Watanabe, Shiho
Yamada, Yuichiro
and
Ogata, Takehiko
2015.
Prediction of on-site depuration of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins accumulated in the scallop Patinopecten yessoensis of Ofunato Bay, Japan.
Fisheries Science,
Vol. 81,
Issue. 4,
p.
635.
Abi-Khalil, Celina
Lopez-Joven, Carmen
Abadie, Eric
Savar, Veronique
Amzil, Zouher
Laabir, Mohamed
and
Rolland, Jean-Luc
2016.
Exposure to the Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Producer Alexandrium catenella Increases the Susceptibility of the Oyster Crassostrea gigas to Pathogenic Vibrios.
Toxins,
Vol. 8,
Issue. 1,
p.
24.
Lassudrie, Malwenn
Soudant, Philippe
Nicolas, Jean-Louis
Miner, Philippe
Le Grand, Jacqueline
Lambert, Christophe
Le Goïc, Nelly
Hégaret, Hélène
and
Fabioux, Caroline
2016.
Exposure to the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella modulates juvenile oyster Crassostrea gigas hemocyte variables subjected to different biotic conditions.
Fish & Shellfish Immunology,
Vol. 51,
Issue. ,
p.
104.
Castrec, J.
Soudant, P.
Payton, L.
Tran, D.
Miner, P.
Lambert, C.
Le Goïc, N.
Huvet, A.
Quillien, V.
Boullot, F.
Amzil, Z.
Hégaret, H.
and
Fabioux, C.
2018.
Bioactive extracellular compounds produced by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum are highly detrimental for oysters.
Aquatic Toxicology,
Vol. 199,
Issue. ,
p.
188.
Basti, Leila
Hégaret, Hélène
and
Shumway, Sandra E.
2018.
Harmful Algal Blooms.
p.
135.
Fernández Robledo, José A.
Yadavalli, Raghavendra
Allam, Bassem
Pales Espinosa, Emmanuelle
Gerdol, Marco
Greco, Samuele
Stevick, Rebecca J.
Gómez-Chiarri, Marta
Zhang, Ying
Heil, Cynthia A.
Tracy, Adrienne N.
Bishop-Bailey, David
and
Metzger, Michael J.
2019.
From the raw bar to the bench: Bivalves as models for human health.
Developmental & Comparative Immunology,
Vol. 92,
Issue. ,
p.
260.
Pousse, Émilien
Flye-Sainte-Marie, Jonathan
Alunno-Bruscia, Marianne
Hégaret, Hélène
Rannou, Éric
Pecquerie, Laure
Marques, Gonçalo M.
Thomas, Yoann
Castrec, Justine
Fabioux, Caroline
Long, Marc
Lassudrie, Malwenn
Hermabessiere, Ludovic
Amzil, Zouher
Soudant, Philippe
and
Jean, Fred
2019.
Modelling paralytic shellfish toxins (PST) accumulation in Crassostrea gigas by using Dynamic Energy Budgets (DEB).
Journal of Sea Research,
Vol. 143,
Issue. ,
p.
152.
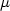 g STX equiv. 100
g−1 wet weight). Then, two different detoxification treatments were
tested and showed detoxification rates greater than those observed in
coastal environments. The first treatment consisted of feeding oysters on
Skeletonema costatum, at a concentration of 2000 cell ml−1 to speed up detoxification rates. The second detoxification method used the same Skeletonema costatum diet, supplemented with silt particles at a concentration of 20 mg L−1. A control was also set up by
placing contaminated oysters in seawater with no additional algal food. The
detoxification experiment lasted 8 days. Toxin contents were analysed by
liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection (LC-FD). The S. costatum diet
significantly reduced the time needed for oysters to reach the sanitary threshold (80 $\mu $
g STX equiv. 100
g−1 wet weight). Then, two different detoxification treatments were
tested and showed detoxification rates greater than those observed in
coastal environments. The first treatment consisted of feeding oysters on
Skeletonema costatum, at a concentration of 2000 cell ml−1 to speed up detoxification rates. The second detoxification method used the same Skeletonema costatum diet, supplemented with silt particles at a concentration of 20 mg L−1. A control was also set up by
placing contaminated oysters in seawater with no additional algal food. The
detoxification experiment lasted 8 days. Toxin contents were analysed by
liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection (LC-FD). The S. costatum diet
significantly reduced the time needed for oysters to reach the sanitary threshold (80 $\mu $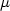 g STX equiv. 100 g−1 wet weight),
but no effect of the silt supplement could be demonstrated conclusively.
These different detoxification methods did not influence toxin
biotransformations as observed in oyster tissues, i.e. epimerisation and
decarbamoylation of gonyautoxins 2 and 3.
g STX equiv. 100 g−1 wet weight),
but no effect of the silt supplement could be demonstrated conclusively.
These different detoxification methods did not influence toxin
biotransformations as observed in oyster tissues, i.e. epimerisation and
decarbamoylation of gonyautoxins 2 and 3.




