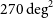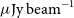117 results
Doug Madsen
-
- Journal:
- Political Science Today / Volume 4 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, p. 21
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Promoting equity, inclusion, and efficiency: A team science approach to the development of authorship guidelines for a multi-disciplinary research team
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 November 2023, e265
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Using clinical decision support to improve urine testing and antibiotic utilization
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 10 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 March 2023, pp. 1582-1586
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Evolutionary Map of the Universe Pilot Survey – ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2022, e055
-
- Article
- Export citation
Introduction to Forecasting the 2022 French Presidential Election
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics / Volume 55 / Issue 4 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2022, pp. 683-686
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Citizen Forecasting: The 2022 French Presidential Election
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics / Volume 55 / Issue 4 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2022, pp. 730-734
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Catatonia: demographic, clinical and laboratory associations
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 6 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2021, pp. 2492-2502
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The ASKAP Variables and Slow Transients (VAST) Pilot Survey
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 October 2021, e054
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Citizen Forecasts of the 2021 German Election
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics / Volume 55 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2021, pp. 97-101
- Print publication:
- January 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Forecasting the 2021 German Election: A Win for Armin Laschet?
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics / Volume 55 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2021, pp. 73-78
- Print publication:
- January 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Forecasting Bloc Support in German Federal Elections: A Political-History Model
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics / Volume 55 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2021, pp. 91-96
- Print publication:
- January 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Evolutionary Map of the Universe pilot survey
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2021, e046
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of mandatory vaccination of healthcare personnel on rates of influenza and other viral respiratory pathogens
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 9 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2021, pp. 1216-1220
- Print publication:
- September 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
A history of high-power laser research and development in the United Kingdom
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 9 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2021, e18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Burden of healthcare-associated infections among hospitalized children within community hospitals participating in an infection control network
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 4 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 March 2021, pp. 510-512
- Print publication:
- April 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Citizen Forecasting 2020: A State-by-State Experiment
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics / Volume 54 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 October 2020, pp. 91-95
- Print publication:
- January 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Political Economy Model: A Blue Wave Forecast For 2020
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics / Volume 54 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 October 2020, pp. 59-62
- Print publication:
- January 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Enhanced Bundled Interventions to Reduce Surgical Site Infections for Patients with Congenital Cardiac Disease
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 41 / Issue S1 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2020, pp. s212-s213
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Early experience with universal preprocedural testing for SARS-CoV-2 in a relatively low-prevalence area
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 42 / Issue 3 / March 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2020, pp. 341-343
- Print publication:
- March 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Effect of Implementation of the American Heart Association Mission Lifeline PreAct Algorithm for Prehospital Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory Activation on the Rate of “False Positive” Activations
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 May 2020, pp. 388-396
- Print publication:
- August 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation