125 results
Enduring the unseen burden: a qualitative analysis on long-term emotional impact of COVID-19 on long-term care workers
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue S1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2024, pp. S512-S513
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Radiofrequency ice dielectric measurements at Summit Station, Greenland
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2023, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Patterns, predictors, and patient-reported reasons for antidepressant discontinuation in the WHO World Mental Health Surveys
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2023, pp. 67-78
-
- Article
- Export citation
Preeclampsia and risk of maternal pulmonary hypertension at high altitude in Bolivia
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 14 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2023, pp. 523-531
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterization and drug release of benzalkonium chloride-loaded organo-palygorskite or organo-montmorillonite
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 July 2023, pp. 102-112
-
- Article
- Export citation
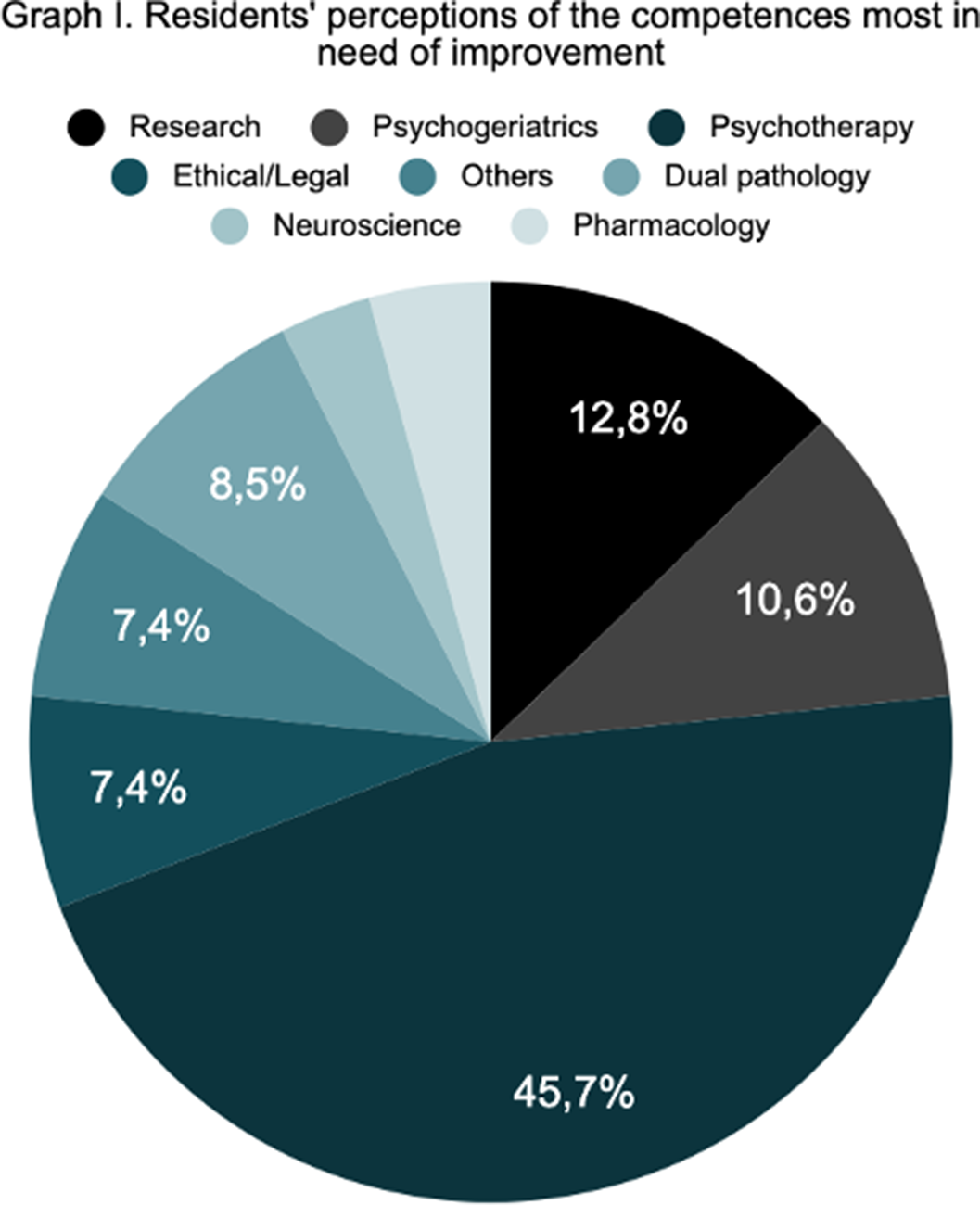
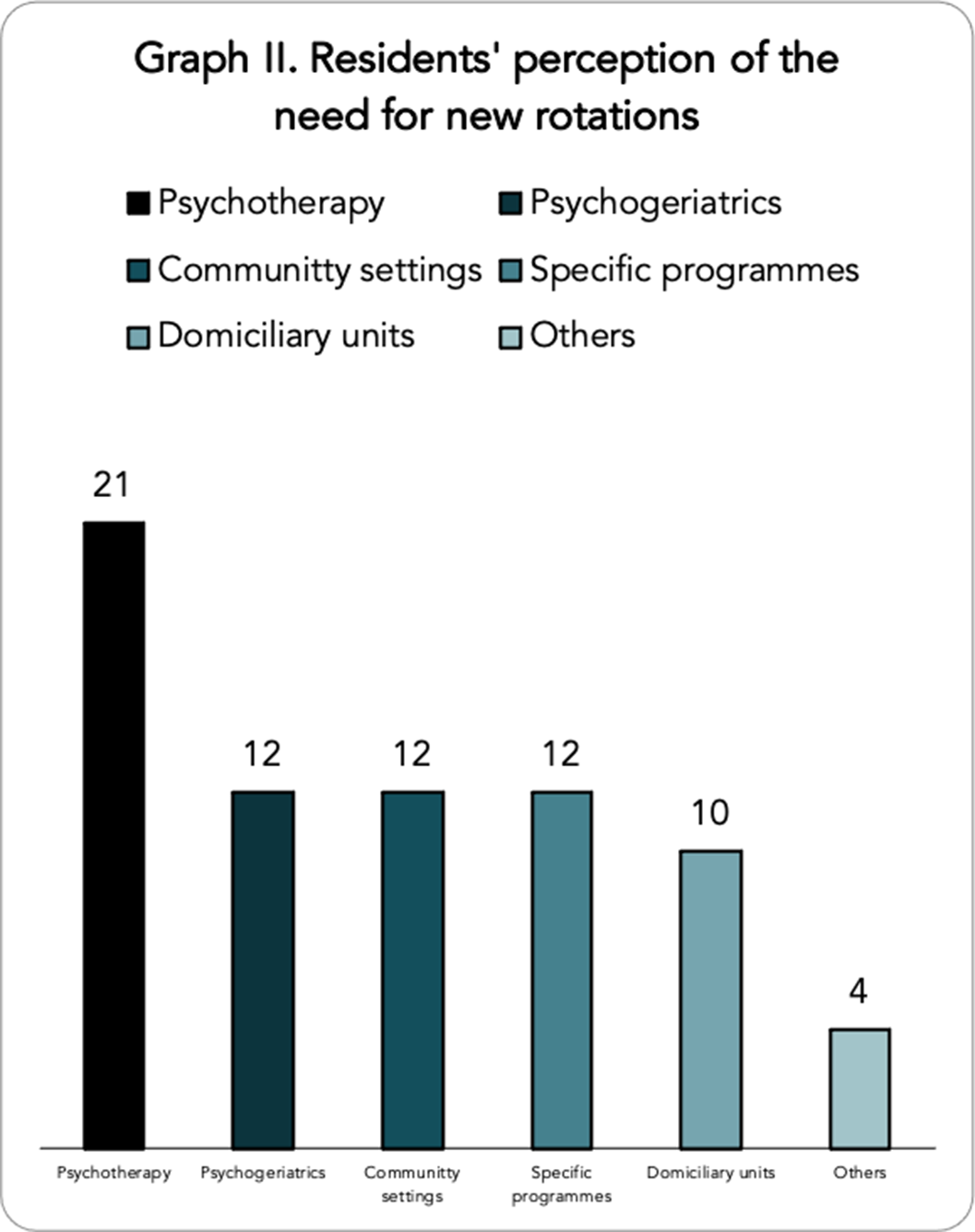
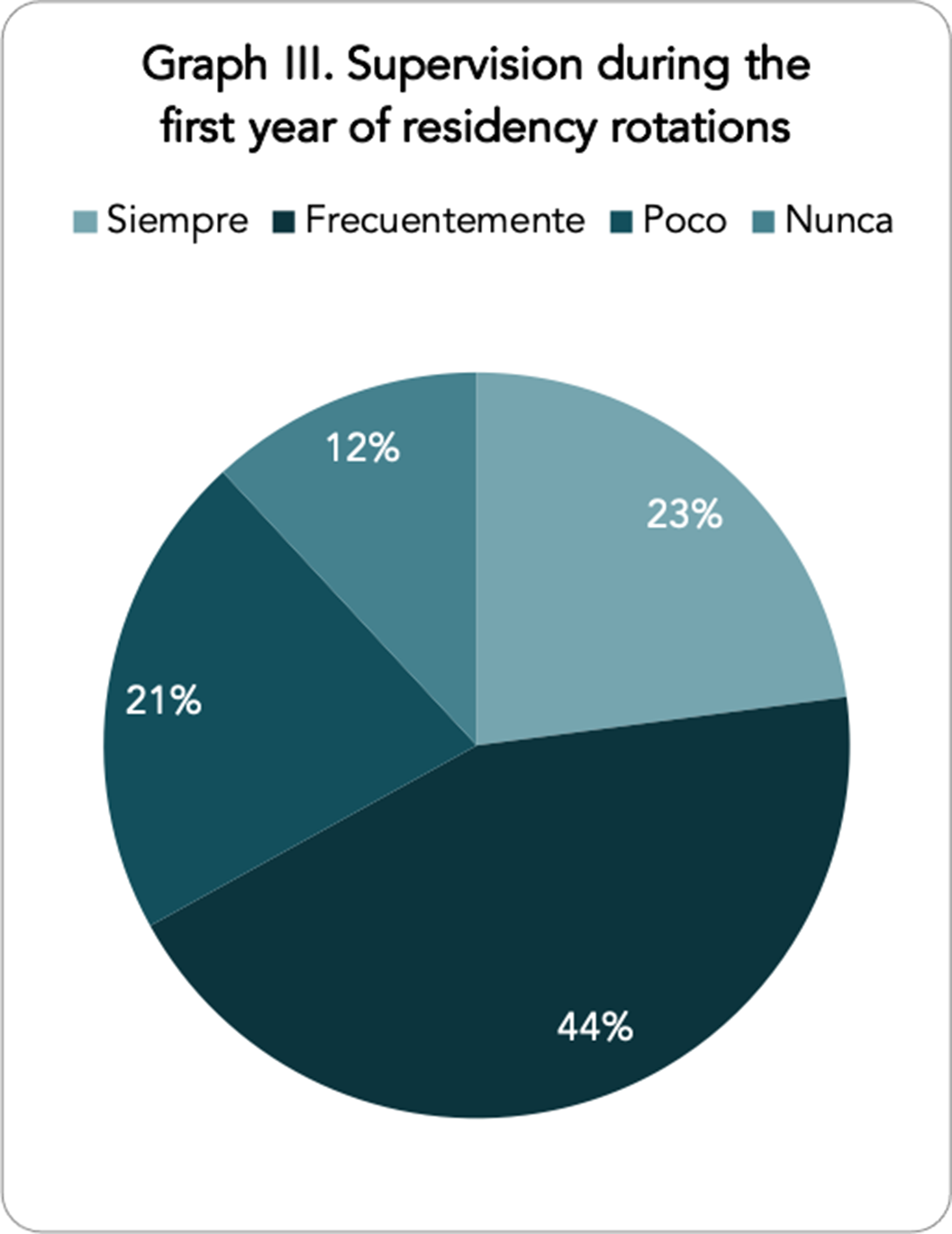
Psychiatry residents’ perceptions of competence acquisition, training programe compliance and clinical supervision in the Spanish psychiatry training system
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S1119-S1121
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
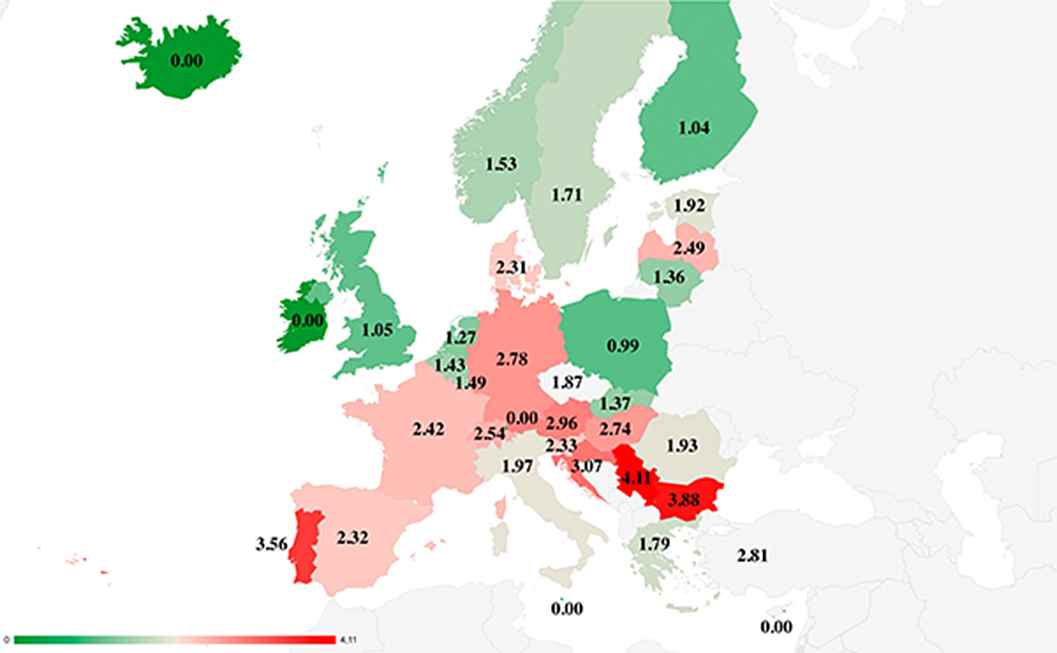
EUROLD: preliminary results of the ecological study on suicide and its associated socioeconomic variables in people over 85 in Europe
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S357
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Cross-sectional study on anxiety in confinement due to covid-19 in a sub-acute and long-stay mental health unit
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S151-S152
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Attitudes towards diversity, equity, and inclusion across the CTSA Programs: Strong but not uniform support and commitment
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2023, e66
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Protestantism in El Salvador: Conventional Wisdom versus Survey Evidence
-
- Journal:
- Latin American Research Review / Volume 28 / Issue 2 / 1993
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 October 2022, pp. 119-140
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
23 - Collaboration and Open Science Initiatives in Primate Research
-
-
- Book:
- Primate Cognitive Studies
- Published online:
- 28 July 2022
- Print publication:
- 11 August 2022, pp 584-608
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Are Anti-Prostitution Advertising Campaigns Effective? An Experimental Study
-
- Journal:
- The Spanish Journal of Psychology / Volume 25 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2022, e21
-
- Article
- Export citation
Eggshell Nanoparticles and Their Effect on Moisture Barrier Properties of Gellan Gum Films by Morphological Analysis
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 908-910
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
In situ, broadband measurement of the radio frequency attenuation length at Summit Station, Greenland
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 68 / Issue 272 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 May 2022, pp. 1234-1242
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Artificial-intelligence and sensing techniques for the management of insect pests and diseases in cotton: a systematic literature review
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 160 / Issue 1-2 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2022, pp. 16-31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neuropsychiatric phenotypes of anti-NMDAR encephalitis: a prospective study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 9 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2022, pp. 4266-4274
-
- Article
- Export citation
Obesity is a strong risk factor for short-term mortality and adverse outcomes in Mexican patients with COVID-19: a national observational study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2021, e109
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Phenotypic diversity and capsaicinoid content of chilli pepper landraces (Capsicum spp.) from the Yucatan Peninsula
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 19 / Issue 2 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2021, pp. 159-166
-
- Article
- Export citation
Examining the association between exposome score for schizophrenia and functioning in schizophrenia, siblings, and healthy controls: Results from the EUGEI study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 64 / Issue 1 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2021, e25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Development and validation of the patient history COVID-19 (PH-Covid19) scoring system: a multivariable prediction model of death in Mexican patients with COVID-19
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 November 2020, e286
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation