41 results
Whole Genome Sequencing to Identify Multiple Clusters of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacterales Cases – Colorado, 2022-2023
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 4 / Issue S1 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2024, p. s110
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Geographical distribution of invasive meningococcal disease and carriage: A spatial analysis
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, e22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Index
-
- Book:
- Children, Childhoods, and Global Politics
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 03 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 09 November 2023, pp 225-231
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Notes on Contributors
-
- Book:
- Children, Childhoods, and Global Politics
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 03 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 09 November 2023, pp vii-xiii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Acknowledgements
-
- Book:
- Children, Childhoods, and Global Politics
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 03 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 09 November 2023, pp xiv-xvi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
PART II - Governed Childhoods
-
- Book:
- Children, Childhoods, and Global Politics
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 03 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 09 November 2023, pp 71-72
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Frontmatter
-
- Book:
- Children, Childhoods, and Global Politics
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 03 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 09 November 2023, pp i-ii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
PART III - Lived Childhoods
-
- Book:
- Children, Childhoods, and Global Politics
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 03 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 09 November 2023, pp 153-154
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
PART I - Imagined Childhoods
-
- Book:
- Children, Childhoods, and Global Politics
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 03 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 09 November 2023, pp 15-16
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Dedication
-
- Book:
- Children, Childhoods, and Global Politics
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 03 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 09 November 2023, pp iii-iv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Introduction: Children and Childhoods in Global Political Perspective
-
-
- Book:
- Children, Childhoods, and Global Politics
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 03 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 09 November 2023, pp 1-14
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contents
-
- Book:
- Children, Childhoods, and Global Politics
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 03 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 09 November 2023, pp v-vi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation

Children, Childhoods, and Global Politics
-
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 03 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 09 November 2023
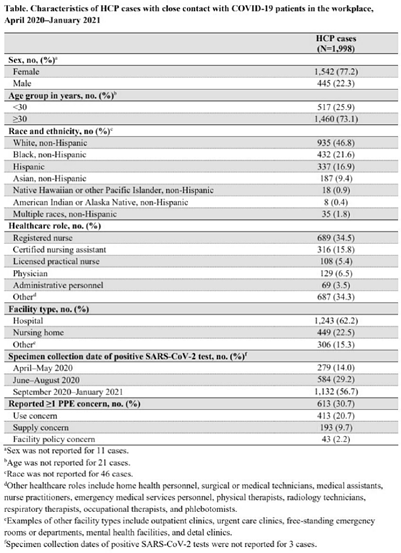
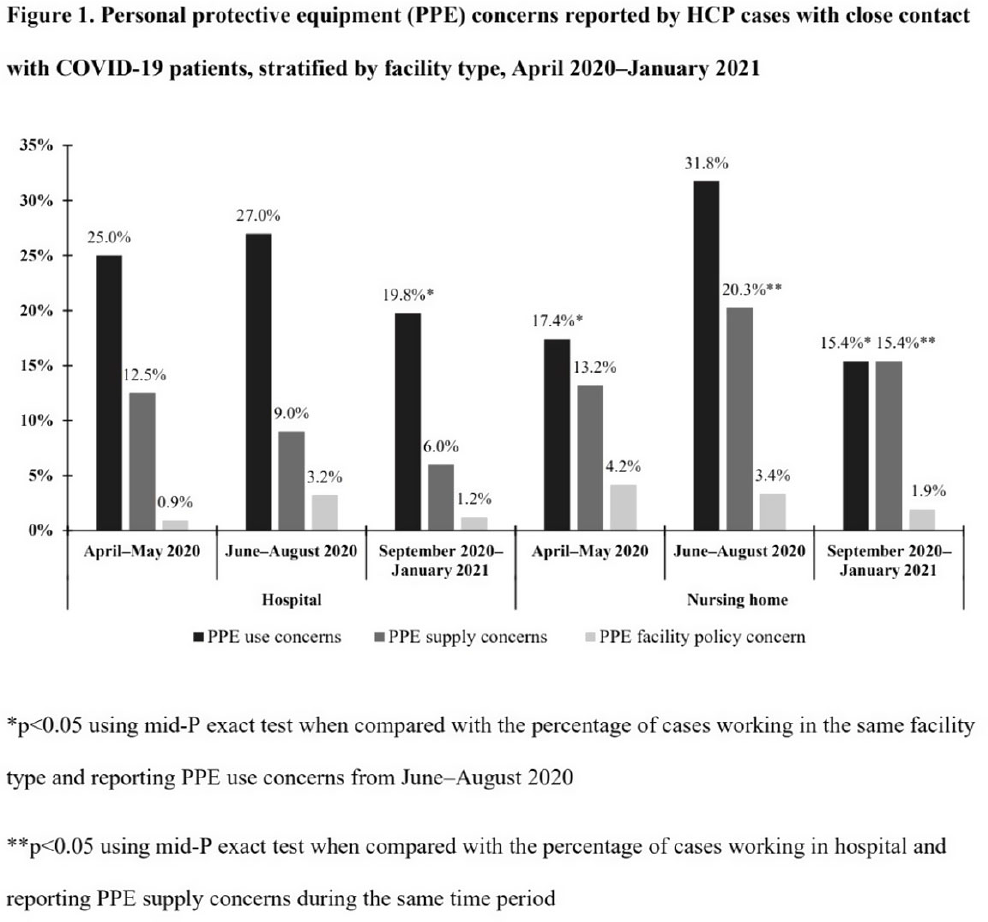
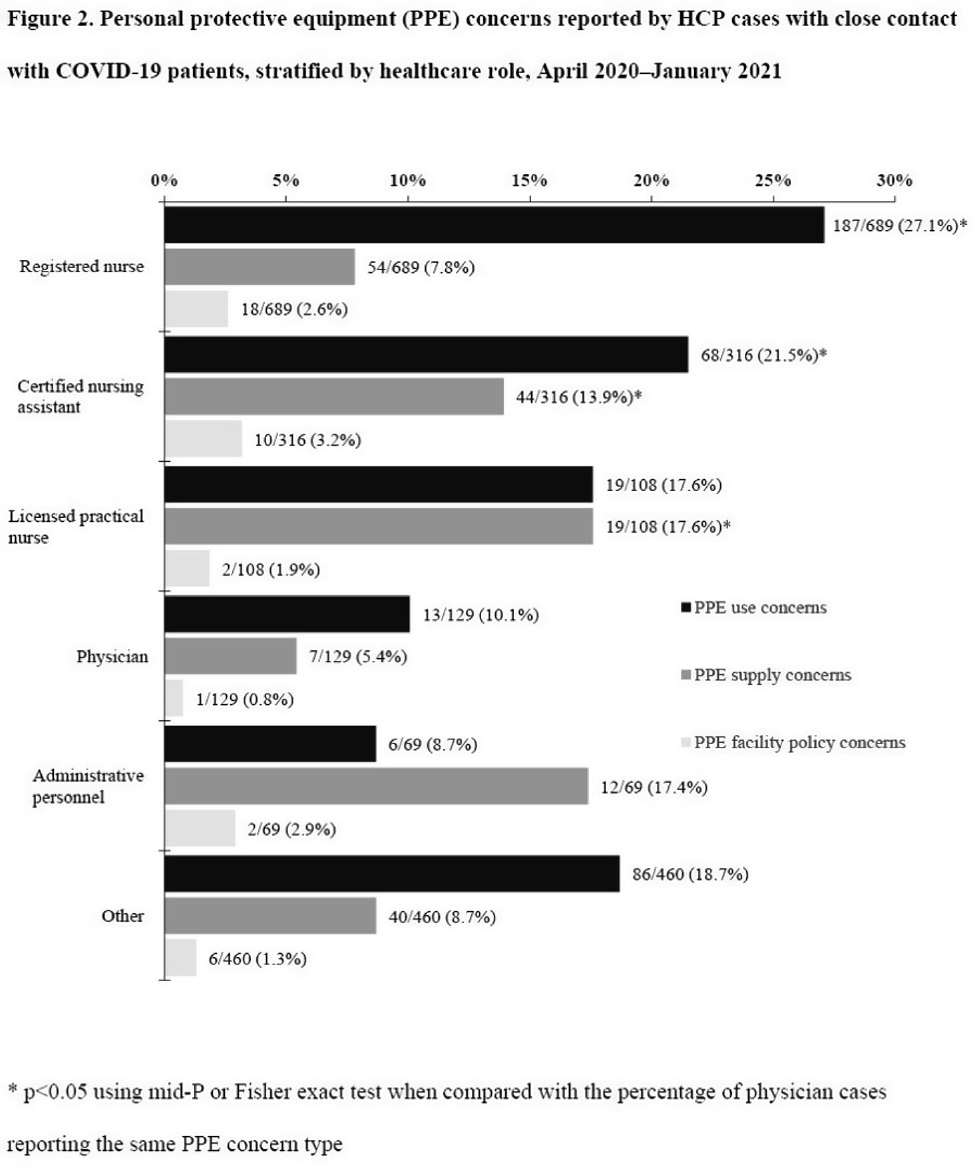
Characteristics of healthcare personnel who reported concerns related to PPE use during care of COVID-19 patients
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 2 / Issue S1 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2022, pp. s8-s9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Practices and activities among healthcare personnel with severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection working in different healthcare settings—ten Emerging Infections Program sites, April–November 2020
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 8 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2021, pp. 1058-1062
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
APSA’s Financial Operations 2016–17
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics / Volume 51 / Issue 2 / April 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 April 2018, pp. 465-469
- Print publication:
- April 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Up the Value Chain: Transition from Law Librarian to Research Analyst
-
- Journal:
- Legal Information Management / Volume 16 / Issue 4 / December 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 December 2016, pp. 207-211
- Print publication:
- December 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Investigating trajectories of social recovery in individuals with first-episode psychosis: A latent class growth analysis
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 207 / Issue 6 / December 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2018, pp. 536-543
- Print publication:
- December 2015
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Women Working as Casual Academics: A Marginalised Group
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian and New Zealand Academy of Management / Volume 4 / Issue 2 / March 1998
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2015, pp. 10-17
-
- Article
- Export citation
Layers of listening: Qualitative analysis of the impact of early intervention services for first-episode psychosis on carers' experiences
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 207 / Issue 2 / August 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2018, pp. 135-142
- Print publication:
- August 2015
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation