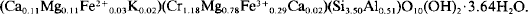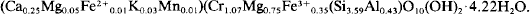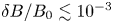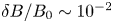766 results
A multi-center validation of the electronic health record admission source and discharge location fields against the clinical notes for identifying inpatients with long-term care facility exposure
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
555 Design Lab Methodology Supports Innovation in Clinical Trials
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 165
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
90 Novel approach for childhood Sjögren’s Disease therapies: multistakeholder design of a series of N-of-1 trials
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Reassessment of the Volkonskoite-Chromian Smectite Nomenclature Problem: Reply
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 36 / Issue 6 / December 1988
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, p. 541
-
- Article
- Export citation
Reassessment of the Volkonskoite-Chromian Smectite Nomenclature Problem
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 35 / Issue 2 / April 1987
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 139-149
-
- Article
- Export citation
Occluded Mica in Hydroxy-Interlayered Vermiculite Grains from a Highly-Weathered Soil
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 40 / Issue 1 / February 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 32-39
-
- Article
- Export citation
One Health governance principles for AMR surveillance: a scoping review and conceptual framework
-
- Journal:
- Research Directions: One Health / Volume 2 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Assessing expectancy and suggestibility in a trial of escitalopram v. psilocybin for depression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 8 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2024, pp. 1717-1724
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
5 Cognitive Rehabilitation Using Teleneuropsychology. A Cohort Study in South America
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, p. 209
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
First mesophotic Ecklonia radiata (Laminariales) records within the iSimangaliso Wetland Park marine-protected area, east coast, South Africa
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 103 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2023, e91
-
- Article
- Export citation
Development, implementation, and dissemination of operational innovations across the trial innovation network
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2023, e251
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fast-ion transport in quasisymmetric equilibria in the presence of a resonant Alfvénic perturbation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2023, 905890515
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
2 - What is a Mask?
-
- Book:
- Masquerades in African Society
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 22 February 2024
- Print publication:
- 17 October 2023, pp 47-78
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contents
-
- Book:
- Masquerades in African Society
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 22 February 2024
- Print publication:
- 17 October 2023, pp vii-x
-
- Chapter
- Export citation

Masquerades in African Society
- Gender, Power and Identity
-
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 22 February 2024
- Print publication:
- 17 October 2023
Dedication
-
- Book:
- Masquerades in African Society
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 22 February 2024
- Print publication:
- 17 October 2023, pp v-vi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
List of Illustrations
-
- Book:
- Masquerades in African Society
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 22 February 2024
- Print publication:
- 17 October 2023, pp xi-xiv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
7 - Masks and Politics
-
- Book:
- Masquerades in African Society
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 22 February 2024
- Print publication:
- 17 October 2023, pp 219-252
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Index
-
- Book:
- Masquerades in African Society
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 22 February 2024
- Print publication:
- 17 October 2023, pp 391-397
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
5 - Death and its Masks
-
- Book:
- Masquerades in African Society
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 22 February 2024
- Print publication:
- 17 October 2023, pp 149-180
-
- Chapter
- Export citation