275 results
Building a Special Pathogen Response Center from the Ground Up
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 4 / Issue S1 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2024, p. s95
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Investigating changes in student mental health and help-seeking behaviour after the introduction of new well-being support services at a UK university
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 3 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2024, e121
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Glastonbury Festival: Medical Care at the World’s Largest Greenfield Music Festival
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 39 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 170-177
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prediction of internalizing and externalizing symptoms in late childhood from attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in early childhood
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Testing residual chloramine levels in tap water across sink locations in a US academic hospital setting
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 March 2024, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association of cognitive reserve with the risk of dementia in the UK Biobank: role of polygenic factors
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 224 / Issue 6 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2024, pp. 213-220
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The impact of minimally invasive surgical approaches on surgical-site infections
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 January 2024, pp. 557-561
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
OP138 Navigating High-Cost Medicines: Promoting Consistent, Evidence-based Use Of High-Cost Medicines In A Fiscally And Equitable Responsible Manner
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 39 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, p. S41
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Strategies to maintain an N95 respirator supply during a pandemic supply-chain shortage
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 December 2023, pp. 688-689
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bacille Calmette-Guérin preparation and intravesical administration to patients with bladder cancer: Risks to healthcare personnel and patients, and mitigation strategies
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 520-525
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of a hard stop for C. difficile testing: Provider uptake and patient outcomes
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s44
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
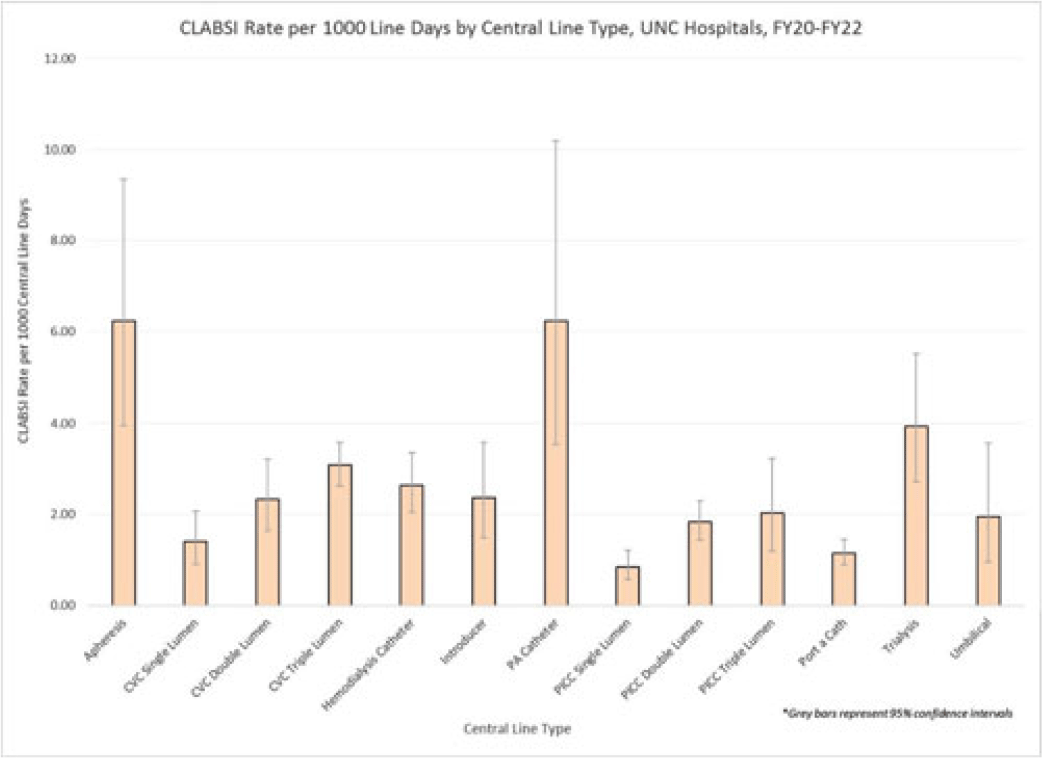
Examining CLABSI rates by central-line type
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. s48-s49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Virtual Interprofessional Education (VIPE)–The VIPE Program: VIPE Security, a Multi-sectoral Approach to Dealing with Complex Wicked Problems
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 38 / Issue S1 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2023, p. s24
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Implementation should be a standard component of practice guidelines and guidance documents
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 9 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 March 2023, pp. 1365-1368
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Digital Livestock Technologies as boundary objects: Investigating impacts on farm management and animal welfare
-
- Journal:
- Animal Welfare / Volume 32 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2023, e17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Blue justice: A review of emerging scholarship and resistance movements
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Coastal Futures / Volume 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2023, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A comparison of methods for microbiologic environmental sampling
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 9 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2022, pp. 1502-1504
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Longitudinal change in serial position scores in older adults with entorhinal and hippocampal neuropathologies
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue 6 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 September 2022, pp. 561-571
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Campaign Disaster Response – What Makes It Different
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2022, e248
-
- Article
- Export citation
A scoping review of best practices in home enteral tube feeding
-
- Journal:
- Primary Health Care Research & Development / Volume 23 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 August 2022, e43
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation