The disjointness graph G = G(𝒮) of a set of segments 𝒮 in 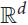 ${\mathbb{R}^d}$,
${\mathbb{R}^d}$, 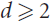 $$d \ge 2$$, is a graph whose vertex set is 𝒮 and two vertices are connected by an edge if and only if the corresponding segments are disjoint. We prove that the chromatic number of G satisfies
$$d \ge 2$$, is a graph whose vertex set is 𝒮 and two vertices are connected by an edge if and only if the corresponding segments are disjoint. We prove that the chromatic number of G satisfies 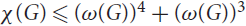 $\chi (G) \le {(\omega (G))^4} + {(\omega (G))^3}$, where ω(G) denotes the clique number of G. It follows that 𝒮 has Ω(n1/5) pairwise intersecting or pairwise disjoint elements. Stronger bounds are established for lines in space, instead of segments.
$\chi (G) \le {(\omega (G))^4} + {(\omega (G))^3}$, where ω(G) denotes the clique number of G. It follows that 𝒮 has Ω(n1/5) pairwise intersecting or pairwise disjoint elements. Stronger bounds are established for lines in space, instead of segments.
We show that computing ω(G) and χ(G) for disjointness graphs of lines in space are NP-hard tasks. However, we can design efficient algorithms to compute proper colourings of G in which the number of colours satisfies the above upper bounds. One cannot expect similar results for sets of continuous arcs, instead of segments, even in the plane. We construct families of arcs whose disjointness graphs are triangle-free (ω(G) = 2), but whose chromatic numbers are arbitrarily large.