Article contents
Magnetotransport in a two-subband AlGaN/GaN heterostructure in the presence of mixed disorder
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 October 2014
Abstract
We present magnetotransport measurements on a high electron density AlGaN/GaN heterostructure with two subbands populated at T = 1.6 K. The transport scattering times, τtr, of each subband are first derived at low magnetic field by taking into account the magneto-intersubband scattering term. Then the quantum scattering times, τq, are extracted from independent Dingle plots, obtained at higher magnetic fields. All scattering times are studied as a function of the total electronic density, increased by the persistent photo-conductivity effect. A standard modelization, based on all common scattering mechanisms, reveals that the transport scattering time is governed by the short-range AlGaN/GaN interface roughness (IR) scattering, whereas the quantum scattering time is due to the smooth potential induced by remote ionized impurities (II) at the GaN surface. This intermediate situation of mixed disorder, where the τtr/τq ratio is greater than one, does not indicate that the mobility is limited by Coulomb scattering. It is due to the unusual condition, τtrII≫τtrIR≫τqII$ {\tau }_{\mathrm{t}r}^{\mathrm{II}}\gg {\tau }_{\mathrm{t}r}^{\mathrm{IR}}\gg {\tau }_{\mathrm{q}}^{\mathrm{II}}$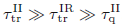 .
.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © EDP Sciences, 2014
References
- 1
- Cited by




