No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
InGaP/GaAs camel-like gate field-effect transistor with InGaAs pseudomorphic doped-channel layer
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 October 2009
Abstract
In this paper, we first fabricate and demonstrate the InGaP/GaAs camel-like gate field-effect transistor with InGaAs pseudomorphic heavy-doped channel. Due to the large gate potential barrier for the use of the n+-GaAs/p+-InGaP/n-GaAs camel-like gate and the thin as well as heavy doping n+-InGaAs channel layer, the effective conduction band discontinuity $(\Delta E_c)$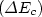 is substantially extended and a high gate turn-on voltage up to 2.0 V is obtained. The device exhibits a relatively broad gate voltage swing resulting from the high gate turn-on voltage. In addition, a maximum drain current of 393 mA/mm and a maximum transconductance of 96 mS/mm are measured. These results indicate that the studied device is suitable for signal amplifier and linear circuit applications.
is substantially extended and a high gate turn-on voltage up to 2.0 V is obtained. The device exhibits a relatively broad gate voltage swing resulting from the high gate turn-on voltage. In addition, a maximum drain current of 393 mA/mm and a maximum transconductance of 96 mS/mm are measured. These results indicate that the studied device is suitable for signal amplifier and linear circuit applications.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © EDP Sciences, 2009




