Article contents
Water-dispersible near-infrared luminescent silicon nanocrystals –immobilization on substrate
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 November 2016
Abstract
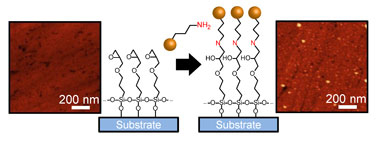
We demonstrate formation of allylamine (AAm) and acrylic acid (AAc)-functionalized colloidal silicon nanocrystals (Si NCs) exhibiting near-infrared (NIR) luminescence and immobilization of the NCs on substrates via covalent bond. The surface functionalization is confirmed by IR absorption spectroscopy and specific binding property of functionalized NCs. Atomic force microscope observations reveal that AAm- and AAc-functionalized Si NCs are chemically immobilized on self-assembled monolayers via covalent bonds. The functionalized Si NCs exhibit photoluminescence in a NIR region (1.5–1.6 eV), which is not significantly affected by the functionalization.
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2016
References
- 4
- Cited by





