No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Weak-Beam Thickness-Fringe Contrast Analysis of Defects in GaN Pyramids
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 July 2020
Extract
The possible dislocations and slip systems in the wurtzite structure are the same as in hcp structure [1]. The Burgers vectors of these dislocations are 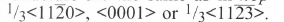 . The
. The 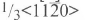 dislocations can lie on either the (0001) basal plane or
dislocations can lie on either the (0001) basal plane or 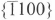 prism planes. The
prism planes. The 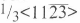 dislocations lie on
dislocations lie on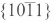 pyramidal planes. TEM studies have revealed that there are predominately three types of dislocations in a wurtzite GaN epilayer which has not been grown by selective overgrowth (e. g. [2, 3]). The majority of the dislocations are threading dislocations with Burgers vector
pyramidal planes. TEM studies have revealed that there are predominately three types of dislocations in a wurtzite GaN epilayer which has not been grown by selective overgrowth (e. g. [2, 3]). The majority of the dislocations are threading dislocations with Burgers vector 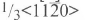 which appear randomly in the epilayer, they result from the growth errors during the growth process. The other two types of dislocation are halflpops with a [0001] or
which appear randomly in the epilayer, they result from the growth errors during the growth process. The other two types of dislocation are halflpops with a [0001] or 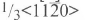 Burgers vector. The [0001] dislocation half-loop lies on the
Burgers vector. The [0001] dislocation half-loop lies on the 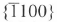 prism plane and the
prism plane and the 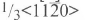 dislocation half-loop lies on the (0001) basal plane which usually appears near the epilayer/substrate interface.
dislocation half-loop lies on the (0001) basal plane which usually appears near the epilayer/substrate interface.
- Type
- Defects in Semiconductors
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Microscopy Society of America




