Article contents
Real double-points of deformations of 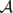 -simple map-germs from
-simple map-germs from 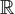 n to
n to 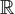 2n
2n
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 April 2007
Abstract
The only stable singularities of a real map-germ 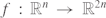 are isolated transverse double-points. All
are isolated transverse double-points. All 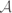 -simple germs f have a deformation with the maximal number d(f) of real double-points (this is a partial generalization to higher n of the result of A'Campo [1] and Gusein-Zade [13] that all plane curve-germs have a deformation with δ real double points, with the extra hypothesis of
-simple germs f have a deformation with the maximal number d(f) of real double-points (this is a partial generalization to higher n of the result of A'Campo [1] and Gusein-Zade [13] that all plane curve-germs have a deformation with δ real double points, with the extra hypothesis of 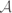 -simplicity). The proof of this result is based on a classification of all
-simplicity). The proof of this result is based on a classification of all 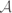 -simple orbits.
-simple orbits.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society , Volume 142 , Issue 2 , March 2007 , pp. 341 - 363
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge Philosophical Society 2007
References
REFERENCES
- 10
- Cited by




