Article contents
Czech trills revisited: An ultrasound EGG and acoustic study
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 July 2014
Abstract
The Czech language has two trills produced with the anterior tongue, represented in the Czech orthography as /r/ and /ř/. The phonetic characterization of the latter trill, currently transcribed in the IPA as [ ], has been especially controversial. The present study uses ultrasound, electroglottography (EGG) and acoustic evidence to examine these trills, with the particular aim of achieving a more phonetically grounded representation of /ř/. In the first part of the paper, ultrasound imaging is used to compare tongue positions between /r/ and /ř/, ruling out tongue height as the key factor distinguishing the two sounds. The second part uses EGG and acoustic evidence to examine phonatory aspects of production. Results implicate vocal fold abduction as the more robust factor distinguishing /r/ from /ř/. Consequently, we posit [
], has been especially controversial. The present study uses ultrasound, electroglottography (EGG) and acoustic evidence to examine these trills, with the particular aim of achieving a more phonetically grounded representation of /ř/. In the first part of the paper, ultrasound imaging is used to compare tongue positions between /r/ and /ř/, ruling out tongue height as the key factor distinguishing the two sounds. The second part uses EGG and acoustic evidence to examine phonatory aspects of production. Results implicate vocal fold abduction as the more robust factor distinguishing /r/ from /ř/. Consequently, we posit [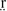 ] as a more appropriate phonetic characterization of /ř/.
] as a more appropriate phonetic characterization of /ř/.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Journal of the International Phonetic Association , Volume 44 , Issue 2 , August 2014 , pp. 115 - 132
- Copyright
- Copyright © International Phonetic Association 2014
References
- 11
- Cited by




