Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 July 2017
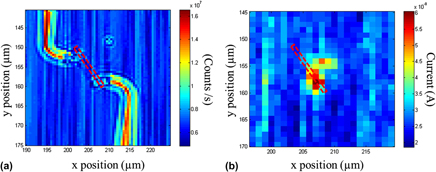
We describe the main experimental challenges toward the metrological calibration of photodetectors based on single semiconductor nanowires, and we propose a method for the quantification of their photoresponse, focusing in particular on GaAs nanowires. Spatially resolved measurements of the device’s photocurrent were performed with a far-field scanning optical setup and a laser excitation at λ = 656 nm. The photoresponse was quantitatively described by fitting the two-dimensional mapping of the photocurrent at different positions along the main nanowire axis. Our results indicate that the device’s photoresponse strongly depends on the position along the nanowire, which is attributed to the inhomogeneous properties of the device’s contacts. Furthermore, we show that its spatial profile across the nanowire can be directly compared with the profile of the laser beam by taking into account the angle between the scanning direction and the main nanowire axis as a geometrical factor. Finally, we discuss the impacts of laser-induced heating effects on the calibration of such nanoscale devices.
Contributing Editor: Winston V. Schoenfeld