Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 September 2017
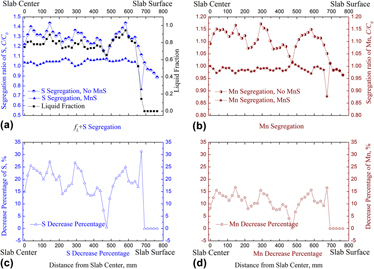
To investigate the solute transport and redistribution in the slab continuous casting processes of high sulfur steel, a three-dimensional model coupling turbulent flow, heat and solute transportation was developed. And then a thermodynamic model for MnS precipitation was established to study the MnS precipitation and distribution in strand on a macroscale and its effect on solute macrosegregation was also explored. The results showed that the temperature and solutes concentration were the main factors for the precipitation of MnS. The effect of temperature was significant when the solid fraction was greater than 0.8. Due to the precipitation of MnS, the segregation ratio of solutes Mn and S on the center line declined from 1.05–1.15 to 0.97–1.01 and from 1.2–1.45 to 1.00–1.08, respectively. And the solute concentration of Mn and S declined and distributed more uniformly in the strand, and the macrosegregation of Mn and S was also suppressed greatly.
Contributing Editor: Jürgen Eckert