Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 October 2017
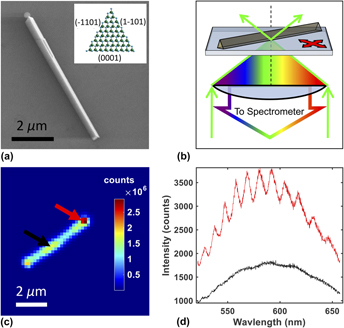
We analyze the microscopic origins of subgap photoexcitations of individual gallium nitride (GaN) triangular cross-section nanowires (NWs), which are highly photoactive over a broadband spectral range. Using confocal hyperspectral photoluminescence (PL) microscopy, mid-gap states on the NWs were excited using subgap illumination, resulting in two distinct PL spectra corresponding to the polar (0001) and the semipolar
 $\left( {\bar 1101} \right)$
/
$\left( {\bar 1101} \right)$
/
 $\left( {1\bar 101} \right)$
surfaces. Emission spectra are well represented by Gaussian functions with fitted centers of 1.99 ± 0.01 eV and 2.26 ± 0.01 eV, respectively. PL collected from the end facets exhibits interference fringes and a relative blue shift. Furthermore, the PL spectrum shifts strongly to the blue when the excitation intensity is increased. These observations are consistent with a qualitative model in which the PL results from excitation into a broad manifold of surface-associated states which are rapidly populated at a high excitation intensity and can couple to etalon modes via longitudinal photon emission.
$\left( {1\bar 101} \right)$
surfaces. Emission spectra are well represented by Gaussian functions with fitted centers of 1.99 ± 0.01 eV and 2.26 ± 0.01 eV, respectively. PL collected from the end facets exhibits interference fringes and a relative blue shift. Furthermore, the PL spectrum shifts strongly to the blue when the excitation intensity is increased. These observations are consistent with a qualitative model in which the PL results from excitation into a broad manifold of surface-associated states which are rapidly populated at a high excitation intensity and can couple to etalon modes via longitudinal photon emission.
Contributing Editor: Johan Brand Malherbe