Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 July 2018
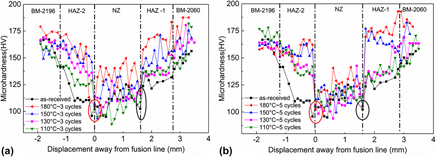
The effects of the thermal cyclic aging treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of 2060 Al–Li alloy laser beam welded joints were investigated. Aging treatments were conducted at different temperatures and for different cycles. Test results showed that the tensile strength of the weld joints increased and the elongation slightly decreased after the thermal cycling treatment. It was also found that the heat affected zone (HAZ) of the welds exhibited a significant increase in microhardness, whilst the microhardness variation of the nondendrite equiaxed zone (EQZ) can be neglected. The strengthening effect of the thermal cycling became more obvious as the temperature and cycles increased. The highest strength of around 513 MPa (96% of the base metal) was obtained at the temperature of 180 °C. Reprecipitation of strengthening phases such as T1 in the HAZ at 180 °C was observed by TEM, which can be considered as the main reason for the strengthening effect of the aging treatment.