Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Krug, Dominik
Yang, Xiang I. A.
de Silva, Charitha M.
Ostilla-Mónico, Rodolfo
Verzicco, Roberto
Marusic, Ivan
and
Lohse, Detlef
2017.
Statistics of turbulence in the energy-containing range of Taylor–Couette compared to canonical wall-bounded flows.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 830,
Issue. ,
p.
797.
de Silva, Charitha M.
Krug, Dominik
Lohse, Detlef
and
Marusic, Ivan
2017.
Universality of the energy-containing structures in wall-bounded turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 823,
Issue. ,
p.
498.
Hwang, Jinyul
and
Sung, Hyung Jin
2018.
Wall-attached structures of velocity fluctuations in a turbulent boundary layer.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 856,
Issue. ,
p.
958.
Lozano-Durán, Adrián
and
Bae, Hyunji Jane
2019.
Error scaling of large-eddy simulation in the outer region of wall-bounded turbulence.
Journal of Computational Physics,
Vol. 392,
Issue. ,
p.
532.
Agostini, Lionel
and
Leschziner, Michael
2019.
The connection between the spectrum of turbulent scales and the skin-friction statistics in channel flow at.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 871,
Issue. ,
p.
22.
Marusic, Ivan
and
Monty, Jason P.
2019.
Attached Eddy Model of Wall Turbulence.
Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 51,
Issue. 1,
p.
49.
Deshpande, Rahul
Monty, Jason P.
and
Marusic, Ivan
2019.
Streamwise inclination angle of large wall-attached structures in turbulent boundary layers.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 877,
Issue. ,
Hwang, Jinyul
and
Sung, Hyung Jin
2019.
Wall-attached clusters for the logarithmic velocity law in turbulent pipe flow.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 5,
Basley, Jérémy
Perret, Laurent
and
Mathis, Romain
2019.
Structure of high Reynolds number boundary layers over cube canopies.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 870,
Issue. ,
p.
460.
Lee, Myoungkyu
and
Moser, Robert D.
2019.
Spectral analysis of the budget equation in turbulent channel flows at high Reynolds number.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 860,
Issue. ,
p.
886.
Baidya, R.
Baars, W. J.
Zimmerman, S.
Samie, M.
Hearst, R. J.
Dogan, E.
Mascotelli, L.
Zheng, X.
Bellani, G.
Talamelli, A.
Ganapathisubramani, B.
Hutchins, N.
Marusic, I.
Klewicki, J.
and
Monty, J. P.
2019.
Simultaneous skin friction and velocity measurements in high Reynolds number pipe and boundary layer flows.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 871,
Issue. ,
p.
377.
Lozano-Durán, Adrián
and
Bae, Hyunji Jane
2019.
Characteristic scales of Townsend’s wall-attached eddies.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 868,
Issue. ,
p.
698.
Lozano-Durán, Adrián
Giometto, Marco G.
Park, George Ilhwan
and
Moin, Parviz
2020.
Non-equilibrium three-dimensional boundary layers at moderate Reynolds numbers.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 883,
Issue. ,
Cheng, Cheng
Li, Weipeng
Lozano-Durán, Adrián
and
Liu, Hong
2020.
On the structure of streamwise wall-shear stress fluctuations in turbulent channel flows.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 903,
Issue. ,
Deshpande, Rahul
Chandran, Dileep
Monty, Jason P.
and
Marusic, Ivan
2020.
Two-dimensional cross-spectrum of the streamwise velocity in turbulent boundary layers.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 890,
Issue. ,
Tanarro, Á.
Vinuesa, R.
and
Schlatter, P.
2020.
Effect of adverse pressure gradients on turbulent wing boundary layers.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 883,
Issue. ,
Yoon, Min
Hwang, Jinyul
Yang, Jongmin
and
Sung, Hyung Jin
2020.
Wall-attached structures of streamwise velocity fluctuations in an adverse-pressure-gradient turbulent boundary layer.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 885,
Issue. ,
Liu, Chang
and
Gayme, Dennice F.
2020.
An input–output based analysis of convective velocity in turbulent channels.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 888,
Issue. ,
Lozano-Durán, Adrián
Bae, H. Jane
and
Encinar, Miguel P.
2020.
Causality of energy-containing eddies in wall turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 882,
Issue. ,
Hwang, Jinyul
Lee, Jae Hwa
and
Sung, Hyung Jin
2020.
Statistical behaviour of self-similar structures in canonical wall turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 905,
Issue. ,
 $u$) in a high-Reynolds-number turbulent boundary layer. A novel experiment employing multiple hot-wire probes was carried out at friction Reynolds numbers ranging from 2400 to 26 000. Taylor’s frozen turbulence hypothesis is used to convert temporal-spanwise information into a 2-D spatial spectrum which shows the contribution of streamwise (
$u$) in a high-Reynolds-number turbulent boundary layer. A novel experiment employing multiple hot-wire probes was carried out at friction Reynolds numbers ranging from 2400 to 26 000. Taylor’s frozen turbulence hypothesis is used to convert temporal-spanwise information into a 2-D spatial spectrum which shows the contribution of streamwise (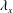 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{x}$) and spanwise (
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{x}$) and spanwise (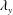 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{y}$) length scales to the streamwise variance at a given wall height (
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{y}$) length scales to the streamwise variance at a given wall height ( $z$). At low Reynolds numbers, the shape of the 2-D spectra at a constant energy level shows
$z$). At low Reynolds numbers, the shape of the 2-D spectra at a constant energy level shows 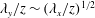 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{y}/z\sim (\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{x}/z)^{1/2}$ behaviour at larger scales, which is in agreement with the existing literature at a matched Reynolds number obtained from direct numerical simulations. However, at high Reynolds numbers, it is observed that the square-root relationship tends towards a linear relationship (
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{y}/z\sim (\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{x}/z)^{1/2}$ behaviour at larger scales, which is in agreement with the existing literature at a matched Reynolds number obtained from direct numerical simulations. However, at high Reynolds numbers, it is observed that the square-root relationship tends towards a linear relationship (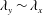 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{y}\sim \unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{x}$), as required for self-similarity and predicted by the attached eddy hypothesis.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{y}\sim \unicode[STIX]{x1D706}_{x}$), as required for self-similarity and predicted by the attached eddy hypothesis.


