Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Yu, Bing
Cong, Hailin
Peng, Qiaohong
Gu, Chuantao
Tang, Qi
Xu, Xiaodan
Tian, Chao
and
Zhai, Feng
2018.
Current status and future developments in preparation and application of nonspherical polymer particles.
Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,
Vol. 256,
Issue. ,
p.
126.
Bounoua, S.
Bouchet, G.
and
Verhille, G.
2018.
Tumbling of Inertial Fibers in Turbulence.
Physical Review Letters,
Vol. 121,
Issue. 12,
Jie, Yucheng
Xu, Chunxiao
Dawson, James R.
Andersson, Helge I.
and
Zhao, Lihao
2019.
Influence of the quiescent core on tracer spheroidal particle dynamics in turbulent channel flow.
Journal of Turbulence,
Vol. 20,
Issue. 7,
p.
424.
Bakhuis, Dennis
Mathai, Varghese
Verschoof, Ruben A.
Ezeta, Rodrigo
Lohse, Detlef
Huisman, Sander G.
and
Sun, Chao
2019.
Statistics of rigid fibers in strongly sheared turbulence.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 4,
Issue. 7,
Zhao, Lihao
Challabotla, Niranjan R.
Andersson, Helge I.
and
Variano, Evan A.
2019.
Mapping spheroid rotation modes in turbulent channel flow: effects of shear, turbulence and particle inertia.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 876,
Issue. ,
p.
19.
Kuperman, Sofia
Sabban, Lilach
and
van Hout, René
2019.
Inertial effects on the dynamics of rigid heavy fibers in isotropic turbulence.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 4,
Issue. 6,
Wu, Gang
Li, Wei
Ni, Weinan
Chen, Lei
Sun, Gang
and
You, Bo
2019.
Preparation of Nonspherical Fluorinated Acrylate Polymer Particles by a “Surface Tension Controlling” Method and Their Applications in Light‐Diffusing Films.
Macromolecular Materials and Engineering,
Vol. 304,
Issue. 8,
Schneiders, Lennart
Fröhlich, Konstantin
Meinke, Matthias
and
Schröder, Wolfgang
2019.
The decay of isotropic turbulence carrying non-spherical finite-size particles.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 875,
Issue. ,
p.
520.
Dotto, Diego
and
Marchioli, Cristian
2019.
Orientation, distribution, and deformation of inertial flexible fibers in turbulent channel flow.
Acta Mechanica,
Vol. 230,
Issue. 2,
p.
597.
Cavaiola, Mattia
Olivieri, Stefano
and
Mazzino, Andrea
2020.
The assembly of freely moving rigid fibres measures the flow velocity gradient tensor.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 894,
Issue. ,
Rosti, Marco E.
Olivieri, Stefano
Banaei, Arash A.
Brandt, Luca
and
Mazzino, Andrea
2020.
Flowing fibers as a proxy of turbulence statistics.
Meccanica,
Vol. 55,
Issue. 2,
p.
357.
Dotto, D.
Soldati, A.
and
Marchioli, C.
2020.
Deformation of flexible fibers in turbulent channel flow.
Meccanica,
Vol. 55,
Issue. 2,
p.
343.
Shaik, Subhani
Kuperman, Sofia
Rinsky, Vladislav
and
van Hout, René
2020.
Measurements of length effects on the dynamics of rigid fibers in a turbulent channel flow.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 11,
Bordoloi, Ankur D.
Variano, Evan
and
Verhille, Gautier
2020.
Lagrangian Time Scale of Passive Rotation for Mesoscale Particles in Turbulence.
Frontiers in Marine Science,
Vol. 7,
Issue. ,
Alipour, Mobin
De Paoli, Marco
Ghaemi, Sina
and
Soldati, Alfredo
2021.
Long non-axisymmetric fibres in turbulent channel flow.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 916,
Issue. ,
Capone, Alessandro
Di Felice, Fabio
and
Alves Pereira, Francisco
2021.
Flow-Particle Coupling in a Channel Flow Laden with Elongated Particles: The Role of Aspect Ratio.
Journal of Marine Science and Engineering,
Vol. 9,
Issue. 12,
p.
1388.
Michel, A.
and
Arcen, B.
2021.
Reynolds number effect on the concentration and preferential orientation of inertial ellipsoids.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 11,
Brizzolara, Stefano
Rosti, Marco Edoardo
Olivieri, Stefano
Brandt, Luca
Holzner, Markus
and
Mazzino, Andrea
2021.
Fiber Tracking Velocimetry for Two-Point Statistics of Turbulence.
Physical Review X,
Vol. 11,
Issue. 3,
Michel, A.
and
Arcen, B.
2021.
Long time statistics of prolate spheroids dynamics in a turbulent channel flow.
International Journal of Multiphase Flow,
Vol. 135,
Issue. ,
p.
103525.
Baker, Lucia J.
and
Coletti, Filippo
2022.
Experimental investigation of inertial fibres and disks in a turbulent boundary layer.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 943,
Issue. ,
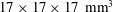 $17\times 17\times 17~\text{mm}^{3}$) was used to measure three-dimensional fibre translational velocities, orientations and rotation rates in near homogeneous isotropic air turbulence (HIT). Flow characteristics were determined from temporally resolved particle image velocimetry measurements. Two sets of rigid, nylon fibres having the same nominal length (0.5 mm) but different diameters (13.7 and
$17\times 17\times 17~\text{mm}^{3}$) was used to measure three-dimensional fibre translational velocities, orientations and rotation rates in near homogeneous isotropic air turbulence (HIT). Flow characteristics were determined from temporally resolved particle image velocimetry measurements. Two sets of rigid, nylon fibres having the same nominal length (0.5 mm) but different diameters (13.7 and 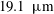 $19.1~\unicode[STIX]{x03BC}\text{m}$), were released in near HIT at a Taylor microscale Reynolds number of
$19.1~\unicode[STIX]{x03BC}\text{m}$), were released in near HIT at a Taylor microscale Reynolds number of 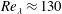 $Re_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}}\approx 130$ and tracked at more than five times the Kolmogorov frequency. The ratio of fibre length to the Kolmogorov length scale was 2.8 and the two sets were characterized by Stokes numbers of 1.35 and 2.44, respectively. As a result of increased inertia, the probability density functions (PDFs) of the fluctuating fibre translational velocities were narrower than the ones of the air and the fibre velocity autocorrelations decreased at a decreasing rate. While fibre orientations in the cameras’ frame of reference were random as a result of the strong turbulence, it was shown that fibres align with the flow to minimize drag. PDFs of the fibre rotation rates indicated the occurrence of extreme rotation rate events. Furthermore, increasing inertia lowered the normalized, mean squared fibre rotation rates in comparison to results obtained for neutrally buoyant fibres having the same aspect ratio and including the effect of preferential alignment. The present results compare well to direct numerical simulations including the effect of fibre inertia.
$Re_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}}\approx 130$ and tracked at more than five times the Kolmogorov frequency. The ratio of fibre length to the Kolmogorov length scale was 2.8 and the two sets were characterized by Stokes numbers of 1.35 and 2.44, respectively. As a result of increased inertia, the probability density functions (PDFs) of the fluctuating fibre translational velocities were narrower than the ones of the air and the fibre velocity autocorrelations decreased at a decreasing rate. While fibre orientations in the cameras’ frame of reference were random as a result of the strong turbulence, it was shown that fibres align with the flow to minimize drag. PDFs of the fibre rotation rates indicated the occurrence of extreme rotation rate events. Furthermore, increasing inertia lowered the normalized, mean squared fibre rotation rates in comparison to results obtained for neutrally buoyant fibres having the same aspect ratio and including the effect of preferential alignment. The present results compare well to direct numerical simulations including the effect of fibre inertia.




