Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Gillissen, J. J. J.
2019.
Two-Dimensional Decaying Elastoinertial Turbulence.
Physical Review Letters,
Vol. 123,
Issue. 14,
Martini, Eduardo
Cavalieri, André V. G.
Jordan, Peter
Towne, Aaron
and
Lesshafft, Lutz
2020.
Resolvent-based optimal estimation of transitional and turbulent flows.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 900,
Issue. ,
Mons, Vincent
and
Marquet, Olivier
2021.
Linear and nonlinear sensor placement strategies for mean-flow reconstruction via data assimilation.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 923,
Issue. ,
Mons, V
Marquet, O
Leclaire, B
Cornic, P
and
Champagnat, F
2022.
Dense velocity, pressure and Eulerian acceleration fields from single-instant scattered velocities through Navier–Stokes-based data assimilation.
Measurement Science and Technology,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 12,
p.
124004.
Wang, Hongping
Liu, Yi
and
Wang, Shizhao
2022.
Dense velocity reconstruction from particle image velocimetry/particle tracking velocimetry using a physics-informed neural network.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 1,
Takahashi, Shun
Misaka, Takashi
Nara, Shotaro
Sugiyama, Naoki
Nohara, Tetsuo
Kawamoto, Yuki
Kuramoto, Yuiki
Obara, Akira
Osada, Rina
Kikuchi, Asuka
Ochiai, Masayuki
Osumi, Kazuo
and
Ishikawa, Naoya
2022.
Estimation of spray flow characteristics using ensemble Kalman filter.
Flow Measurement and Instrumentation,
Vol. 88,
Issue. ,
p.
102247.
Takahashi, Shun
Misaka, Takashi
Nara, Shotaro
Sugiyama, Naoki
Nohara, Tetsuo
Kawamoto, Yuki
Kuramoto, Yuiki
Obara, Akira
Osada, Rina
Kikuchi, Asuka
Ochiai, Masayuki
Osumi, Kazuo
and
Ishikawa, Naoya
2022.
Estimation of Spray Flow Characteristics Using Ensemble Kalman Filter.
SSRN Electronic Journal ,
Kontogiannis, Alexandros
Elgersma, Scott V.
Sederman, Andrew J.
and
Juniper, Matthew P.
2022.
Joint reconstruction and segmentation of noisy velocity images as an inverse Navier–Stokes problem.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 944,
Issue. ,
Abassi, Mohamed Amine
Wang, Qi
and
Liu, Xiaofeng
2023.
Data Assimilation for isotropic turbulent flow and Pressure Computation using Omnidirectional Integration.
Burman, Erik
Gillissen, Jurriaan J. J.
and
Oksanen, Lauri
2023.
Stability estimate for scalar image velocimetry.
Journal of Inverse and Ill-posed Problems,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 6,
p.
811.
Liu, Zhifeng
and
Yang, Yue
2023.
Construction of the vortex-surface field from tomographic particle image velocimetry data of flow past a vortex generator.
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 64,
Issue. 6,
Wang, Haoyu
Hong, Liu
and
Chamorro, Leonardo P.
2024.
Micro-Scale Particle Tracking: From Conventional to Data-Driven Methods.
Micromachines,
Vol. 15,
Issue. 5,
p.
629.
Steinfurth, B.
and
Weiss, J.
2024.
Assimilating experimental data of a mean three-dimensional separated flow using physics-informed neural networks.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 36,
Issue. 1,
He, Chuangxin
Zeng, Xin
Wang, Peng
Wen, Xin
and
Liu, Yingzheng
2024.
Four-dimensional variational data assimilation of a turbulent jet for super-temporal-resolution reconstruction.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 978,
Issue. ,
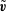 $\tilde{\boldsymbol{v}}$, that are measured using particle image velocimetry (PIV). The method minimises the space–time integral of the difference between the reconstruction
$\tilde{\boldsymbol{v}}$, that are measured using particle image velocimetry (PIV). The method minimises the space–time integral of the difference between the reconstruction  $\boldsymbol{u}$ and
$\boldsymbol{u}$ and 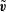 $\tilde{\boldsymbol{v}}$, under the constraint, that
$\tilde{\boldsymbol{v}}$, under the constraint, that  $\boldsymbol{u}$ satisfies conservation of mass and momentum. We apply the method to synthetic velocimetry data, in a two-dimensional turbulent flow, where realistic PIV noise is generated by computationally mimicking the PIV measurement process. The method performs optimally when the assimilation integration time is of the order of the flow correlation time. We interpret these results by comparing them to one-dimensional diffusion and advection problems, for which we derive analytical expressions for the reconstruction error.
$\boldsymbol{u}$ satisfies conservation of mass and momentum. We apply the method to synthetic velocimetry data, in a two-dimensional turbulent flow, where realistic PIV noise is generated by computationally mimicking the PIV measurement process. The method performs optimally when the assimilation integration time is of the order of the flow correlation time. We interpret these results by comparing them to one-dimensional diffusion and advection problems, for which we derive analytical expressions for the reconstruction error.



