No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Coupled bulk and interfacial transport of surfactants governs the settling of a drop towards a wall
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 May 2024
Abstract
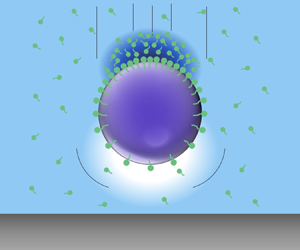
Surfactant-like impurities are omnipresent in multiphase emulsions and may substantially affect the motion of small droplets by altering their interfacial properties. Usually these surfactants are soluble in the bulk and undergo adsorption–desorption onto the interface which modifies their surface concentration and hence their overall influence on droplet motion. Yet, the impact of the bulk solubility and transport of surfactants on droplet dynamics, especially in the presence of bounding walls, remains poorly understood. As such, in this article, we assess the impact of bulk soluble surfactants on the settling of a spherical drop towards a plane wall. We consider coupled bulk and interfacial transport of surfactants, mediated by adsorption–desorption processes and construct a semi-analytical framework for arbitrary values of ‘bulk interaction parameter’, which dictates the strength of adsorption–desorption kinetics compared with bulk diffusion. Our results indicate that while mass exchange between the bulk and the interface can remobilize the drop, a finite bulk diffusion rate restricts this process and therefore slows down the drop. This also results in bulk concentration depletion near the south pole and accumulation near the north pole, the extent of which becomes strongly asymmetric with an enhanced intensity of depletion, as the drop approaches the wall. Presence of the wall and bulk solubility are found to aid each other towards remobilizing the drop by aptly modifying the interfacial concentration. Our results may provide fundamental insights into the kinetics of surfactant-laden drops, with potential applications in food and pharmaceutical industries, separation processes, etc.
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Cambridge University Press





