No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Imbibition and collapse between swelling fibres
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 December 2023
Abstract
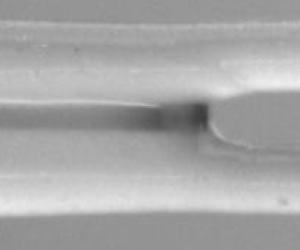
While capillary imbibition in tubes or porous materials has been studied extensively in the past, less attention has been paid to imbibition into a swellable porous material. However, swelling is commonly observed when a polymeric network, such as the cellulose composing paper fibres or sponges, absorbs a solvent. The incompressibility of the fluid leads to an elastic expansion of the polymeric matrix. In a porous material, swelling can affect the geometry of the pores, thus affecting the capillary flow. To describe this complex problem, we propose a model experiment, namely the capillary imbibition in a model pore composed of two parallel and stretched elastomeric fibres. In this configuration, one can observe both the progression of a capillary meniscus and the swelling of the fibres. We show that swelling enables a capillary imbibition for fibres placed further apart than the critical distance existing for non-swelling fibres. In this swelling-dominated regime, we identify a new imbibition dynamic at constant velocity which we rationalize using a linear poro-elastic theory. Finally, we describe the elastocapillary collapse of our model pore which is observed when capillary forces overcome the restoring tension force within the fibres.
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2023. Published by Cambridge University Press





