Article contents
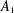 $A_{1}$-TYPE SUBGROUPS CONTAINING REGULAR UNIPOTENT ELEMENTS
$A_{1}$-TYPE SUBGROUPS CONTAINING REGULAR UNIPOTENT ELEMENTS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 April 2019
Abstract
Let 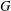 $G$ be a simple exceptional algebraic group of adjoint type over an algebraically closed field of characteristic
$G$ be a simple exceptional algebraic group of adjoint type over an algebraically closed field of characteristic 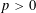 $p>0$ and let
$p>0$ and let 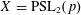 $X=\text{PSL}_{2}(p)$ be a subgroup of
$X=\text{PSL}_{2}(p)$ be a subgroup of 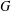 $G$ containing a regular unipotent element
$G$ containing a regular unipotent element  $x$ of
$x$ of 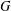 $G$. By a theorem of Testerman,
$G$. By a theorem of Testerman,  $x$ is contained in a connected subgroup of
$x$ is contained in a connected subgroup of 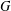 $G$ of type
$G$ of type 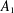 $A_{1}$. In this paper we prove that with two exceptions,
$A_{1}$. In this paper we prove that with two exceptions, 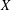 $X$ itself is contained in such a subgroup (the exceptions arise when
$X$ itself is contained in such a subgroup (the exceptions arise when 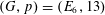 $(G,p)=(E_{6},13)$ or
$(G,p)=(E_{6},13)$ or 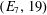 $(E_{7},19)$). This extends earlier work of Seitz and Testerman, who established the containment under some additional conditions on
$(E_{7},19)$). This extends earlier work of Seitz and Testerman, who established the containment under some additional conditions on 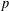 $p$ and the embedding of
$p$ and the embedding of 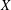 $X$ in
$X$ in 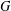 $G$. We discuss applications of our main result to the study of the subgroup structure of finite groups of Lie type.
$G$. We discuss applications of our main result to the study of the subgroup structure of finite groups of Lie type.
MSC classification
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Creative Commons
- This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution licence (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted re-use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- Copyright
- © The Author(s) 2019
References
- 4
- Cited by




