Article contents
Weighted Birkhoff ergodic theorem with oscillating weights
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 September 2017
Abstract
We consider sequences of Davenport type or Gelfond type and prove that sequences of Davenport exponent larger than 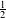 $\frac{1}{2}$ are good sequences of weights for the ergodic theorem, and that the ergodic sums weighted by a sequence of strong Gelfond property are well controlled almost everywhere. We prove that for any
$\frac{1}{2}$ are good sequences of weights for the ergodic theorem, and that the ergodic sums weighted by a sequence of strong Gelfond property are well controlled almost everywhere. We prove that for any  $q$-multiplicative sequence, the Gelfond property implies the strong Gelfond property and that sequences realized by dynamical systems can be fully oscillating and have the Gelfond property.
$q$-multiplicative sequence, the Gelfond property implies the strong Gelfond property and that sequences realized by dynamical systems can be fully oscillating and have the Gelfond property.
- Type
- Original Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press, 2017
References
- 7
- Cited by




