Article contents
Synthesis of Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanorings for BSA Protein Adsorption
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 January 2024
Abstract
The adsorption of bovine serum albumin (BSA) protein is important for protein research but remains a great challenge. Here, the hydrothermal method and calcination in a hydrogen-argon mixed atmosphere were used to obtain ordered mono-crystalline magnetic Fe3O4 nanorings with controllable size and uniform structure, which were applied to the adsorption of BSA protein. The results showed that the magnetic Fe3O4 nanorings prepared have the advantages of good crystallinity, controllable morphology, and excellent magnetic response. The Fe3O4 nanorings had an outer diameter of ~160–180 nm, inner diameter of ~80–110 nm, and height of 70 to ~110 nm. The amount of BSA adsorbed by magnetic Fe3O4 nanorings increased with increasing protein concentration; when the concentration of BSA was ~2.75 mg·mL-1 the adsorption amount approached saturation. When the pH value of the solution was ~5, the Fe3O4 nanorings absorption of BSA was greatest. With increasing adsorption time, the amount adsorbed increased gradually. Adsorption equilibrium was reached after 3 h. According to the formula, the saturated adsorption capacity of BSA per gram of magnetic Fe3O4 nanorings was 325.2 mg.
Graphical Abstract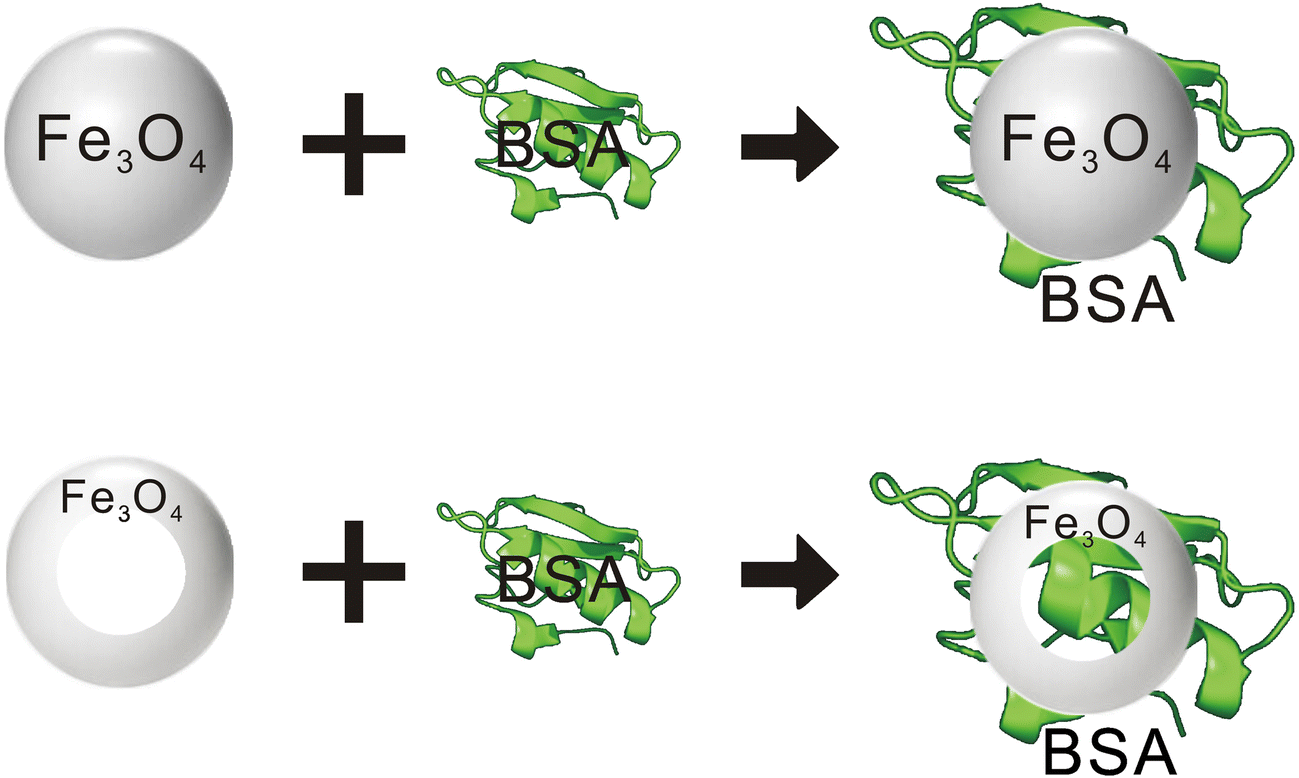
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Clay Minerals Society 2019
Footnotes
This paper was originally presented during the World Forum on Industrial Minerals, held in Qing Yang, China, October 2018.
References
- 2
- Cited by




