Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Long, Botao
and
Wu, Wei
2017.
Isometry groups of twisted reduced group C∗-algebras.
International Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 14,
p.
1750101.
Goswami, Debashish
and
Mandal, Arnab
2017.
Quantum isometry groups of dual of finitely generated discrete groups and quantum groups.
Reviews in Mathematical Physics,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 03,
p.
1750008.
Latrémolière, Frédéric
2019.
Actions of categories by Lipschitz morphisms on limits for the Gromov–Hausdorff propinquity.
Journal of Geometry and Physics,
Vol. 146,
Issue. ,
p.
103481.
Latrémolière, Frédéric
2019.
Convergence of Cauchy sequences for the covariant Gromov–Hausdorff propinquity.
Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications,
Vol. 469,
Issue. 1,
p.
378.
Long, Botao
and
Wu, Wei
2020.
Lipschitz isometries of compact quantum metric spaces.
Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications,
Vol. 486,
Issue. 2,
p.
123917.
AGUILAR, KONRAD
2021.
INDUCTIVE LIMITS OF C*-ALGEBRAS AND COMPACT QUANTUM METRIC SPACES.
Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society,
Vol. 111,
Issue. 3,
p.
289.
Long, Botao
and
Wu, Wei
2021.
Twisted bounded-dilation group C*-algebras as C*-metric algebras.
Science China Mathematics,
Vol. 64,
Issue. 3,
p.
547.
Latrémolière, Frédéric
2021.
Convergence of Spectral Triples on Fuzzy Tori to Spectral Triples on Quantum Tori.
Communications in Mathematical Physics,
Vol. 388,
Issue. 2,
p.
1049.
Bassi, Jacopo
Conti, Roberto
Farsi, Carla
and
Latrémolière, Frédéric
2023.
Isometry groups of inductive limits of metric spectral triples and Gromov–Hausdorff convergence.
Journal of the London Mathematical Society,
Vol. 108,
Issue. 4,
p.
1488.
Rieffel, Marc A.
2023.
Convergence of Fourier truncations for compact quantum groups and finitely generated groups.
Journal of Geometry and Physics,
Vol. 192,
Issue. ,
p.
104921.
Farsi, Carla
Latrémolière, Frédéric
and
Packer, Judith
2024.
Convergence of inductive sequences of spectral triples for the spectral propinquity.
Advances in Mathematics,
Vol. 437,
Issue. ,
p.
109442.
沈, 文涛
2024.
The Lower Semicontinuity of Seminorms on Crossed Product <i>C</i><sup>*</sup>-Algebras of Integer Group.
Advances in Applied Mathematics,
Vol. 13,
Issue. 06,
p.
2943.
Latrémolière, Frédéric
2024.
Continuity of the spectrum of Dirac operators of spectral triples for the spectral propinquity.
Mathematische Annalen,
Vol. 389,
Issue. 1,
p.
765.
 $\mathbb{L}$ be a length function on a group
$\mathbb{L}$ be a length function on a group  $G$, and let
$G$, and let 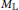 ${{M}_{\mathbb{L}}}$ denote the operator of pointwise multiplication by
${{M}_{\mathbb{L}}}$ denote the operator of pointwise multiplication by  $\mathbb{L}$ on
$\mathbb{L}$ on 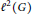 ${{\ell }^{2}}\left( G \right)$. Following Connes,
${{\ell }^{2}}\left( G \right)$. Following Connes, 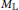 ${{M}_{\mathbb{L}}}$ can be used as a “Dirac” operator for the reduced group
${{M}_{\mathbb{L}}}$ can be used as a “Dirac” operator for the reduced group 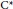 ${{C}^{*}}$-algebra
${{C}^{*}}$-algebra 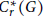 $C_{r}^{*}\left( G \right)$. It defines a Lipschitz seminorm on
$C_{r}^{*}\left( G \right)$. It defines a Lipschitz seminorm on 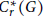 $C_{r}^{*}\left( G \right)$, which defines a metric on the state space of
$C_{r}^{*}\left( G \right)$, which defines a metric on the state space of 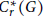 $C_{r}^{*}\left( G \right)$. We show that for any length function satisfying a strong form of polynomial growth on a discrete group, the topology from this metric coincides with the weak-
$C_{r}^{*}\left( G \right)$. We show that for any length function satisfying a strong form of polynomial growth on a discrete group, the topology from this metric coincides with the weak- $*$ topology (a key property for the definition of a “compact quantum metric space”). In particular, this holds for all word-length functions on finitely generated nilpotent-by-finite groups.
$*$ topology (a key property for the definition of a “compact quantum metric space”). In particular, this holds for all word-length functions on finitely generated nilpotent-by-finite groups.



