No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
ALGORITHM TO CONSTRUCT INTEGRO SPLINES
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 September 2021
Abstract
We study some properties of integro splines. Using these properties, we design an algorithm to construct splines 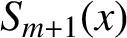 $S_{m+1}(x)$
of neighbouring degrees to the given spline
$S_{m+1}(x)$
of neighbouring degrees to the given spline 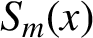 $S_m(x)$
with degree m. A local integro-sextic spline is constructed with the proposed algorithm. The local integro splines work efficiently, that is, they have low computational complexity, and they are effective for use in real time. The construction of nonlocal integro splines usually leads to solving a system of linear equations with band matrices, which yields high computational costs.
$S_m(x)$
with degree m. A local integro-sextic spline is constructed with the proposed algorithm. The local integro splines work efficiently, that is, they have low computational complexity, and they are effective for use in real time. The construction of nonlocal integro splines usually leads to solving a system of linear equations with band matrices, which yields high computational costs.
Keywords
MSC classification
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Australian Mathematical Society 2021





