Book contents
- The Epilepsy Prescriber’s Guide to Antiepileptic Drugs
- The Epilepsy Prescriber’s Guide to Antiepileptic Drugs
- Copyright page
- Contents
- Preface
- Introduction
- Acetazolamide
- ACTH
- Brivaracetam
- Carbamazepine
- Clobazam
- Clonazepam
- Diazepam
- Eslicarbazepine Acetate
- Ethosuximide
- Felbamate
- Fosphenytoin
- Gabapentin
- Lacosamide
- Lamotrigine
- Levetiracetam
- Lorazepam
- Methsuximide
- Midazolam
- Oxcarbazepine
- Paraldehyde
- Perampanel
- Phenobarbital
- Phenytoin
- Piracetam
- Pregabalin
- Primidone
- Rufinamide
- Stiripentol
- Sulthiame
- Tiagabine
- Topiramate
- Valproate
- Vigabatrin
- Zonisamide
- Abbreviations
- Interaction table
- Index
- References
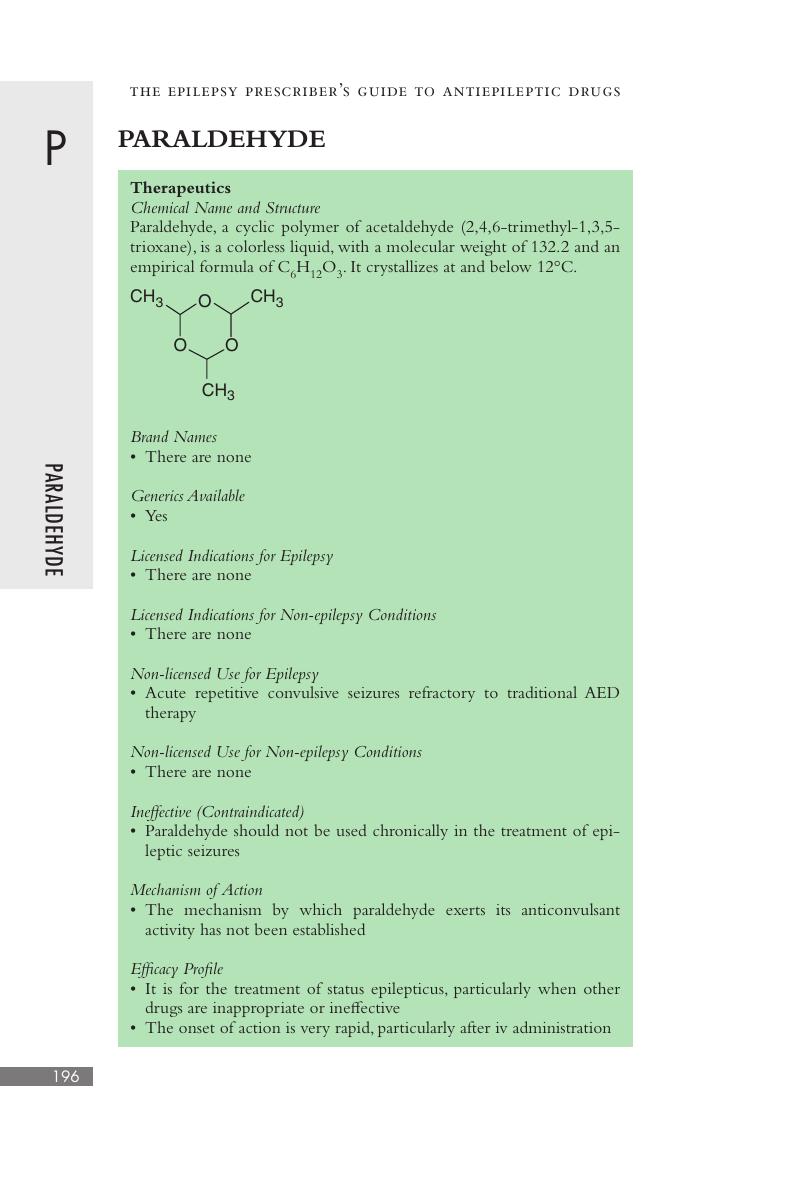
Paraldehyde
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 June 2018
- The Epilepsy Prescriber’s Guide to Antiepileptic Drugs
- The Epilepsy Prescriber’s Guide to Antiepileptic Drugs
- Copyright page
- Contents
- Preface
- Introduction
- Acetazolamide
- ACTH
- Brivaracetam
- Carbamazepine
- Clobazam
- Clonazepam
- Diazepam
- Eslicarbazepine Acetate
- Ethosuximide
- Felbamate
- Fosphenytoin
- Gabapentin
- Lacosamide
- Lamotrigine
- Levetiracetam
- Lorazepam
- Methsuximide
- Midazolam
- Oxcarbazepine
- Paraldehyde
- Perampanel
- Phenobarbital
- Phenytoin
- Piracetam
- Pregabalin
- Primidone
- Rufinamide
- Stiripentol
- Sulthiame
- Tiagabine
- Topiramate
- Valproate
- Vigabatrin
- Zonisamide
- Abbreviations
- Interaction table
- Index
- References
Summary
- Type
- Chapter
- Information
- The Epilepsy Prescriber's Guide to Antiepileptic Drugs , pp. 196 - 203Publisher: Cambridge University PressPrint publication year: 2018

