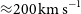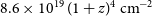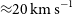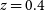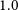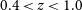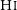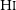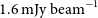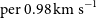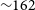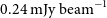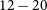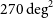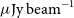87 results
Bereavement guilt among young adults impacted by caregivers’ cancer: Associations with attachment style, experiential avoidance, and psychological flexibility
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Health Equity Engineering: Optimizing Hope for a New Generation of Healthcare
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2024, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
5 The Association of Neighborhood Socioeconomic Deprivation with Neurocognition in a Diverse Cohort of Middle- and Older-Aged Persons Living with and Without HIV
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 685-687
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
90 Feasibility of Repeated Remote Memory Assessment with Mobile Devices to Detect Subtle Cognitive Decline in Older Adults
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 492-493
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Cross-cultural evaluation of learning and memory using a consonant-vowel-consonant trigram list
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue 10 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, pp. 922-932
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
We’ll take it from here: Veterans Affairs OPAT management of home IV therapy initiated at community hospitals
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2023, e197
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Radiofrequency ice dielectric measurements at Summit Station, Greenland
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2023, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A call to action: Taking the untenable out of women professors’ pregnancy, postpartum, and caregiving demands
-
- Journal:
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology / Volume 16 / Issue 2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2023, pp. 187-210
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
“It Is A Carrot-Stick Model”: A Qualitative Study of Rural-Serving Clinician and Rural-Residing Veteran Perceptions of Requirements to Quit Smoking prior to Elective Surgery
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Smoking Cessation / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e10
- Print publication:
- 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Development and application of novel performance validity metrics for computerized neurocognitive batteries
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue 8 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2022, pp. 789-797
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Myocardial perfusion and function dichotomy in growth restricted preterm infants
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 14 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2022, pp. 302-310
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: Public release of H i data for almost 600 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e058
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Evolutionary Map of the Universe Pilot Survey – ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2022, e055
-
- Article
- Export citation
In situ, broadband measurement of the radio frequency attenuation length at Summit Station, Greenland
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 68 / Issue 272 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 May 2022, pp. 1234-1242
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The importance of biodiversity risks
-
- Journal:
- British Actuarial Journal / Volume 27 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2022, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The First Large Absorption Survey in H i (FLASH): I. Science goals and survey design
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2022, e010
-
- Article
- Export citation
The 2nd Annual US Celebration of World Hospice and Palliative Care Day: A virtual coming together to support equity in palliative care access
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care / Volume 20 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2022, pp. 307-312
-
- Article
- Export citation
GASKAP-HI pilot survey science I: ASKAP zoom observations of Hi emission in the Small Magellanic Cloud
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2022, e005
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The ASKAP Variables and Slow Transients (VAST) Pilot Survey
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 October 2021, e054
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Evolutionary Map of the Universe pilot survey
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2021, e046
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation