Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 March 2021
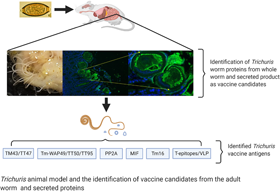
Trichuriasis known as whipworm infection caused by Trichuris trichiura, is a highly prevalent soil-transmitted helminthiasis in low- and middle-income countries located in tropical and subtropical areas and affecting approximately 360 million people. Children typically harbour the largest burden of T. trichiura and they are usually co-infected with other soil-transmitted helminth (STH), including Ascaris lumbricoides and hookworm. The consequences of trichuriasis, such as malnutrition and physical and cognitive growth restriction, lead to a massive health burden in endemic regions. Despite the implementation of mass drug administration of anthelminthic treatment to school-age children, T. trichiura infection remains challenging to control due to the low efficacy of current drugs as well as high rates of post-treatment re-infection. Thus, the development of a vaccine that would induce protective immunity and reduce infection rate or community faecal egg output is essential. Hurdles for human whipworm vaccine development include the lack of suitable vaccine antigen targets and animal models for human T. trichiura infection. Instead, rodent whipworm T. muris infected mouse models serve as a major surrogate for testing immunogenicity and efficacy of vaccine candidates. In this review, we summarize recent advances in animal models for T. trichiura antigen discovery and testing of vaccine candidates, while providing an overall view of the current status of T. trichiura vaccine development.