Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Fan, Aihua
2017.
Fully oscillating sequences and weighted multiple ergodic limit.
Comptes Rendus Mathematique,
Vol. 355,
Issue. 8,
p.
866.
Shi, Ruxi
2018.
Equivalent definitions of oscillating sequences of higher orders.
Collectanea Mathematica,
Vol. 69,
Issue. 3,
p.
395.
Akiyama, Shigeki
and
Jiang, Yunping
2019.
Higher Order Oscillation and Uniform Distribution.
Uniform distribution theory,
Vol. 14,
Issue. 1,
p.
1.
Xu, Leiye
2019.
Möbius disjointness for topological models of ergodic measure-preserving systems with quasi-discrete spectrum.
Journal of Differential Equations,
Vol. 266,
Issue. 7,
p.
3883.
Fan, Aihua
and
Konieczny, Jakub
2019.
On uniformity of q‐multiplicative sequences.
Bulletin of the London Mathematical Society,
Vol. 51,
Issue. 3,
p.
466.
Huang, Wen
Wang, Zhiren
and
Ye, Xiangdong
2019.
Measure complexity and Möbius disjointness.
Advances in Mathematics,
Vol. 347,
Issue. ,
p.
827.
FAN, AI-HUA
2019.
Weighted Birkhoff ergodic theorem with oscillating weights.
Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems,
Vol. 39,
Issue. 5,
p.
1275.
Jiang, Yujiao
and
Lü, Guangshi
2019.
On automorphic analogues of the Möbius randomness principle.
Journal of Number Theory,
Vol. 197,
Issue. ,
p.
268.
Lü, Guangshi
2020.
Aperiodicity of signs of Hecke eigenvalues.
Monatshefte für Mathematik,
Vol. 191,
Issue. 1,
p.
187.
Fuhrmann, Gabriel
and
Gröger, Maik
2020.
Constant length substitutions, iterated function systems and amorphic complexity.
Mathematische Zeitschrift,
Vol. 295,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
1385.
MCNAMARA, REDMOND
2021.
Sarnak’s conjecture for sequences of almost quadratic word growth.
Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems,
Vol. 41,
Issue. 10,
p.
3060.
Huang, Wen
Liu, Jianya
and
Wang, Ke
2021.
Möbius disjointness for skew products on a circle and a nilmanifold.
Discrete & Continuous Dynamical Systems,
Vol. 41,
Issue. 8,
p.
3531.
Li, Jian
Oprocha, Piotr
and
Zhang, Guohua
2022.
Quasi-graphs, zero entropy and measures with discrete spectrum.
Nonlinearity,
Vol. 35,
Issue. 3,
p.
1360.
Bárány, Balázs
Rams, Michaƚ
and
Shi, Ruxi
2022.
On the multifractal spectrum of weighted Birkhoff averages.
Discrete & Continuous Dynamical Systems,
Vol. 42,
Issue. 5,
p.
2461.
Gu, Weichen
and
Wei, Fei
2022.
Möbius Disjointness for a Class of Exponential Functions.
The Quarterly Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 73,
Issue. 4,
p.
1427.
Fan, Aihua
Fan, Shilei
Ryzhikov, Valery V.
and
Shen, Weixiao
2022.
Bohr chaoticity of topological dynamical systems.
Mathematische Zeitschrift,
Vol. 302,
Issue. 2,
p.
1127.
Sun, Wenbo
2023.
Sarnak's Conjecture for nilsequences on arbitrary number fields and applications.
Advances in Mathematics,
Vol. 415,
Issue. ,
p.
108883.
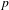 $p$
-adic polynomials of integral coefficients, all
$p$
-adic polynomials of integral coefficients, all
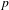 $p$
-adic rational maps with good reduction, all automorphisms of the
$p$
-adic rational maps with good reduction, all automorphisms of the
 $2$
-torus with zero topological entropy, all diagonalizable affine maps of the
$2$
-torus with zero topological entropy, all diagonalizable affine maps of the
 $2$
-torus with zero topological entropy, all Feigenbaum maps, and all orientation-preserving circle homeomorphisms.
$2$
-torus with zero topological entropy, all Feigenbaum maps, and all orientation-preserving circle homeomorphisms.

