Cows' milk protein allergy (CMPA) is defined by the occurrence of clinical symptoms related to the abnormal immune response of the host after ingestion of these proteins. The prevalence of CMPA ranges between 2 and 7 %(Reference Høst1), depending on the methods of recruitment, age distribution of populations studied and diagnostic criteria. The prevalence of a food allergy as perceived by the child's parents is higher than that of the actual food allergy(Reference Noimark and Cox2, Reference Tuokkola, Kaila and Pietinen3). Clinical symptoms may affect the skin (urticaria, atopic dermatitis), the digestive tract (vomiting, diarrhoea) as well as the respiratory tract (rhinitis, asthma), often combined together and associated with failure to thrive and anaemia, and according to various syndromes corresponding to the immune mechanism, IgE-mediated, non-IgE-mediated, or both. The diagnosis of CMPA, suggested clinically, may be aided by results obtained from skin tests (prick tests), specific IgE assays and/or patch tests, which only indicate sensitisation. The diagnosis requires the elimination–challenge procedure, a standard diagnostic tool for food allergy, without which the elimination diet is unjustified, and sometimes harmful. Confirmation of CMPA will impose the elimination of cows' milk proteins (CMP) from the patient's diet. Milk proteins are allergens of animal origin, potentially cross-reacting with the milk of other mammals, and CMPA may be the first manifestation of a polysensitisation whereby children may also be allergic to other major allergens, such as soya, egg, peanut or wheat. This explains why the dietary management of CMPA exhibits some uncertainties, difficult to foresee in a given child, and justifying individual and cautious approaches in the introduction of complementary foods. The natural progression of CMPA most often leads to a spontaneous recovery, with a time line that varies from case to case, and which depends mainly on the immunological process (whether IgE-mediated or not), and on the specific type of milk protein involved. The acquisition of oral tolerance and the maintenance thereof seems to be favoured by a regular exposure to the allergens. The dichotomous situation ‘allergic child equals strict diet; cured child equals normal diet’, although still relevant for infants, has been replaced, beyond a certain age, by the concept of ‘dose tolerated by the child’.
The aim of the present review by the Committee on Nutrition of the French Society of Paediatrics (CNFSP) is to clarify the dietary management (with reference to nature, duration, benefits and risks) of CMPA based on the current understanding of this particular allergy, taking into account both the recent progress in the understanding of the disease and the dietary changes involved.
Nutritional consequences of cows' milk protein allergy
Clinical symptoms of CMPA occur in a child receiving a cows' milk-based infant formula (IF) and/or dairy products and are very protean, including cutaneous manifestations, digestive manifestations related to ‘gastroenterocolitic’ and ‘enteropathic’ phenomena, as well as respiratory manifestations. Human milk also contains foreign proteins in small amounts, to which some children may react: if allergy symptoms occur in an exclusively breast-fed child, CMPA should be discussed.
The nutritional impact of CMPA varies considerably in both expression and intensity, and should be systematically evaluated. It depends not only on the extent of intestinal mucosal inflammation, which may induce malabsorption and/or protein-losing enteropathy, but on the occurrence of skin protein losses as well, as in the case of atopic dermatitis. Published data do not allow distinguishing between what is related to mucosal inflammation and its consequences, to vomiting or to a decreased dietary intake. Surprisingly, very few studies have addressed Fe deficiency, the most common nutritional deficiency associated with CMPA. Anaemia may not be just a nutritional consequence, but also due to blood loss and, as such, representative of more than just an Fe deficiency. In itself, isolated Fe-deficiency anaemia can reveal CMPA(Reference Savilahti4). In an Italian study, 25 % of patients with CMPA were Fe deficient(Reference Ferrara, Coppola and Coppola5). Some cases of infant CMPA manifest themselves in a failure to thrive. The long-term consequences of these nutritional deficiencies are not yet completely known.
Dietary management of cows' milk protein allergy before the onset of complementary feeding
In the case of CMPA, breast-feeding, if still possible, is the first choice. When breast-feeding is not possible or not desired, cows' milk-based IF should be replaced by a substitute, an extensively hydrolysed formula (eHF) based on the extensive hydrolysis of a source protein, usually from milk, in order to considerably reduce allergenicity, as explained below. eHF are the only formulae suitable to feed infants with documented CMPA and should allow normal growth and development. These eHF are distinct from partially hydrolysed formulae, referred to as ‘hypoallergenic’ in some countries, not suitable for the treatment of CMPA, and to be used only to feed non-breast-fed infants considered to be at risk for allergy(Reference Chouraqui, Dupont and Bocquet6). However, it should be noted that there are no physical, chemical or immunological criteria that allow any regulatory distinction between a partially hydrolysed formula and an eHF(7).
Breast-feeding
When the diagnosis of CMPA is suggested during breast-feeding, a trial elimination diet, with the strict elimination of CMP from the mother's diet for 2–3 weeks, should result in the prompt disappearance of symptoms in the child(Reference Vandenplas, Koletzko and Isolauri8). The mother should receive daily Ca supplements during the elimination diet. If the elimination diet is ineffective, it should be discontinued, and the possibility of an alternative disease should be examined. If symptoms improve or clear up during the elimination diet, it is then possible to attempt a gradual reintroduction of CMP into the maternal diet that should not exceed the maximal dose tolerated by the child.
When the diagnosis of CMPA is made following the first feeds with cows' milk-based IF in a breast-fed infant, the continuation of breast-feeding is ideally recommended, without any elimination in the maternal diet since breast milk was previously well tolerated.
European regulations
Children with CMPA must be fed with nutritionally adequate hydrolysates in the replacement of cows' milk-based IF, cows' milk and dairy products. The composition of the hydrolysates used within the European Union (EU) must meet the requirements of the Commission Directive 1999/21/EC of 25 March 1999 on dietary foods for special medical purposes(9).
The European Commission has limited the content of immunoreactive proteins in the hydrolysates to < 1 % of the total content of N-containing substances and determines the adequacy and safety of an hydrolysate based on (1) experimental studies (oral administration should not induce sensitisation, in animals, to the intact proteins from which the hydrolysate is manufactured) and (2) clinical trials, showing that the hydrolysate is tolerated by more than 90 % of infants presenting with hypersensitivity to the proteins from which the hydrolysate is manufactured(10).
Cows' milk protein hydrolysates
eHF comply with the European regulations for biological standards and animal testing. Unfortunately, very few clinical studies have confirmed their efficacy in the treatment of CMPA.
eHF available in many European countries (Table 1) are all (except Nutrilon Pepti®, named Galliagène® in France; Nutricia Advanced Medical Nutrition, Strombeek-Bever, Belgium) lactose-free, and the protein portion consists of either cows' milk casein hydrolysates (Nutramigen® and Pregestimil® (Mead Johnson, Evansville, IN, USA), with the same hydrolysed protein, Allernova® (United Pharmaceuticals, Paris, France) and Nutriben CMPA® (Madrid Spain)), or cows' milk whey protein hydrolysates (Pepti-Junior® (Lactalis Nutrition Santé, Laval, France), Alfaré® and Althéra®, Nutrilon Pepti®).
Table 1 Extensively hydrolysed formulae (eHF) and amino acid (AA)-based formulae (AAF) available in Europe for children with cows' milk protein allergy*
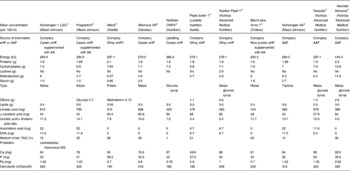
* Based on products also available in France; only infant formula (0–6 months) when applicable.
† Hydrosylate identical to that of Althéra®.
The recommendation made in 1993 by the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, namely to use formulae containing proteins of a molecular weight (MW) of < 1300 Da(Reference Aggett, Haschke and Heine11), is relevant in terms of quality control (verification of reproducibility among manufacturing processes) but does not allow to predict the degree of immunogenicity or potential reaction in a given child(Reference Høst, Koletzko and Dreborg12). It is noticeable that this 1 % threshold of immunoreactive proteins in the hydrolysates, dating back to the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) recommendation of 1999(Reference Høst, Koletzko and Dreborg12), does not rely on any clinical trials of good scientific quality. Such clinical trials, for which recommendations have been made in 2004(Reference Taylor, Hefle and Bindslev-Jensen13), have not yet been performed. Suitable thresholds of reaction, still unknown, however, may be closer to 1/1000(Reference Moneret-Vautrin and Kanny14).
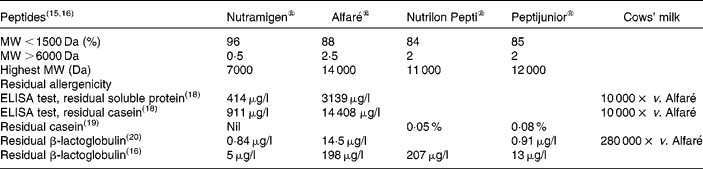
The MW of peptides and residual allergenicity of the cows' milk hydrolysates are shown in Table 2, where the lowest residual allergenicity is observed with Nutramigen®, which is lower than that of Alfaré®, Peptijunior® and Nutrilon Pepti®, respectively(Reference Bindels and Boerma15–Reference Mäkinen-Kiljunen and Sorva20). Recent modifications of the hydrolysate used in Alfaré led to a reduction of its MW profile, similar to that of the newly launched Althéra® (Nestlé, Vevey, Switzerland), characterised by a median peptide size of 362 Da, with 99·7 % of peptides < 2400 Da(Reference Niggemann, von Berg and Bollrath21).
Table 2 Residual molecular weights (MW) of peptides and residual allergenicity of cows' milk hydrolysates
Diagnostic tests, Radio AllergoSorbenk test (RAST)-specific and/or skin prick test of the aforementioned eHF, were performed in children presenting with IgE-mediated CMPA (Table 3). In three separate studies, the skin prick test was positive with Nutramigen® in zero out of ten(Reference Høst and Samuelsson22), four out of ten(Reference Sampson, Bernhisel-Broadbent and Yang23), and one out of forty-two(Reference Oldaeus, Björkstén and Einarsson24) children tested, respectively. In three other studies, it was positive with Nutramigen® in zero out of fifteen and with Alfaré® in one out of fifteen(Reference Oldaeus, Bradley and Björkstén25); with Nutramigen® in zero out of seventeen and with Alfaré® in two out of seventeen(Reference Wahn, Wahl and Rugo17); and with Nutrilon Pepti® in six out of thirty-one children(Reference Giampietro, Kjellman and Oldaeus26). RAST was more frequently positive, in two out of fifteen children tested with Nutramigen® and seven out of fifteen with Peptijunior®(Reference Dean, Adler and Ruge27), four out of ten with Nutramigen® and five out of ten with Alfaré®(Reference Wahn, Wahl and Rugo17).
Table 3 Analysis of clinical studies assessing the efficacy of extensive protein hydrolysates: percentage of patients with no reaction during different evaluation tests (clinical symptoms, skin prick tests (SPT), oral food challenge (OFC) and RAST)
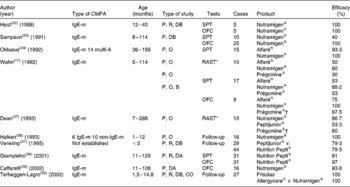
CMPA, cows' milk protein allergy; IgE-m, IgE-mediated; P, prospective; R, randomised; DB, double blind; multi-A, multi-allergic; O, open; B, blind; CO, cross-over.
* Radio AllergoSorbent test (RAST), specific IgE (Phadia®; Stockholm, Sweden).
† At the time of the study, beef collagen hydrolysate.
The allergic efficacy of eHF was tested in ten studies, almost all involving a small number of children of various ages (usually older than 6 months) with IgE-mediated allergies (Table 2). In six studies conducted on Nutramigen®, and which included a total of ninety-seven children, an efficacy of 93·8–100 % has been shown(Reference Wahn, Wahl and Rugo17, Reference Høst and Samuelsson22, Reference Sampson, Bernhisel-Broadbent and Yang23, Reference Halken, Høst and Hansen28–Reference Terheggen-Lagro, Khouw and Schaafsma30). In two studies conducted on Nutrilon Pepti® that included seventy-five children, an efficacy of 79·5(Reference Verwimp, Bindels and Barents31) and 98 %(Reference Giampietro, Kjellman and Oldaeus26) has been shown, respectively. A study carried out on Peptijunior® included twenty-nine children, all < 3 months of age, and showed an efficacy of 79·3 %(Reference Verwimp, Bindels and Barents31). A study undertaken with Alfaré® included eight children, and showed efficacy in six cases(Reference Wahn, Wahl and Rugo17). The recently launched eHF Althéra®, with a low peptide MW, identical to the reformulated Alfaré®, induced no reaction, similarly to the amino acid-based formula (AAF) reference product in thirty-four infants with CMPA demonstrated by a double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenge(Reference Niggemann, von Berg and Bollrath21). A study conducted on Frisolac Allergycare® (Friesland Nutrition, Leeuwarden, The Netherlands), which included twenty-seven children over the age of 1·5 years, showed an efficacy of 75 %(Reference Terheggen-Lagro, Khouw and Schaafsma30).
The CNFSP regrets the small number of studies and the insufficient statistical power of the few existing studies on cows' milk protein hydrolysates. Most relevant studies are relatively old and were carried out using product formulations differing from those of currently marketed products. If, based on the experience of most clinicians, these products have been well tolerated by most allergic children, the Committee nonetheless recommends that their compliance with the current efficacy rules expressed in the European regulations be investigated in all.
Free amino acid-based formulae
Formulae based on free amino acids (AAF; Neocate®, Neocate Advance® (Nutricia Advanced Medical Nutrition) after 1 year, Nutramigen AA® (Mead Johnson)) are devoid of intact proteins and peptides. The only traces that may be present in these formulae would come from contaminants in the starch and lipid parts (including soya in Nutramigen AA®). A systematic review of twenty studies on the use of an AAF (Neocate®) in patients presenting with CMPA concluded as to its efficacy, tolerance and safety(Reference Hill, Murch and Rafferty32). When the persistence of symptoms under eHF feeding is suggestive of allergy to eHF, particularly in IgE-mediated gastroenteroproctitis with a failure to thrive or severe atopic eczema, resolution of symptoms and catch-up growth may be obtained with the use of Neocate®(Reference de Boissieu and Dupont33, Reference Niggemann, Binder and Dupont34). A study has shown that Nutramigen AA® is efficient and allows normal growth in infants with CMPA(Reference Burks, Jones and Berseth35). However, no data are available in infants with allergy to eHF.
Rice protein hydrolysates
Protein hydrolysates not originating from cows' milk have become available. A prospective study of the tolerance to a rice eHF supplemented with lysine and threonine enrolled ninety-nine children with CMPA and a mean age of 3 years(Reference Fiocchi, Restani and Bernardini36). Although patients often developed serum anti-rice protein IgE (RAST: twenty-one out of ninety-one; immunoblotting: seventy out of ninety-six), only six of them had clinical reactions to the eHF, which makes the formula suitable for children with CMPA. A rice protein hydrolysate supplemented with lysine, threonine and tryptophan, first marketed in Spain, is now available in several European countries (Table 1). A study of this eHF has shown that it was well tolerated by 90 % of children (mean age 4·4 months) presenting with CMPA(Reference Reche, Pascual and Fiandor37).
Soya protein-based infant formulae
Soya protein-based IF are dietary products without CMP, enriched in methionine, carnitine, Fe and Zn. They contain phytates, Al and high amounts of phyto-oestrogens, the potential effects of which are still poorly understood in children(Reference Bocquet, Bresson and Briend38–Reference Bhatia and Greer40). Infants with CMPA may also be allergic to soya protein. This association was observed in one study in 14 % of children aged 3–41 months presenting with IgE-mediated CMPA(Reference Zeiger, Sampson and Bock41), and 10 % in another study, with little difference between IgE-mediated and non-IgE-mediated CMPA, but with a higher prevalence among infants under 6 months of age(Reference Klemola, Vanto and Juntunen-Backman42). Soya protein-based IF are not indicated in the treatment of infants with CMPA below 6 months of age(Reference Bocquet, Bresson and Briend38–Reference Bhatia and Greer40), owing to a high level of phytates and a high phyto-oestrogen intake resulting from exclusive formula feeding(Reference Agostoni, Axelsson and Goulet39).
Inappropriate products
The composition (i.e. in terms of protein, fat, folic acid and mineral content) of milk from other mammals (goat, sheep, donkey, horse, etc.) makes them nutritionally unsuitable when they are the only food provided to infants, whether the infant is allergic or not.
Industrial juices made of soya, rice, almond, coconut or chestnut are improperly called ‘milks’ and usually sold in organic outlets. They are totally unsuitable to meet infant nutritional needs and should therefore not be used. Severe nutritional disorders, such as kwashiorkor(Reference Liu, Howard and Mancini43) and rickets(Reference Noimark and Cox2, Reference Fox, Du Toit and Lang44, Reference Yu, Pekeles and Legault45), have been described in infants with CMPA fed such an inappropriate elimination diet.
Recommendations for the use of hydrolysates by expert committees and scientific societies
Recommendations for the use of hydrolysates in CMPA are limited. The choice of a hydrolysate varies from one country to another or within the same country. A recent paper describing the identification and management of CMPA depicts all the eHF available for children in the UK(Reference du Toit, Meyer and Shah46).
An international working group has released draft recommendations for the management of CMPA in infants, whether breast fed or not. In case of suspicion of CMPA of moderate severity, the working group recommends using an eHF based on soluble protein or casein; in severe cases (either where there is a life-threatening risk or a severe failure to thrive), the recommendation is to readily use an AAF(Reference Vandenplas, Koletzko and Isolauri8).
A group of Australian experts suggests eHF as the first resort in infants under 6 months of age, in cases where a current allergy exists, and in cases concerning gastrointestinal symptoms and atopic eczema. The group recommends soya protein-based IF in infants over 6 months with presently existing reactions to CMP, and in the case of gastrointestinal symptoms or atopic dermatitis with normal growth. In the case of anaphylaxis, the group recommends AAF as a first choice, until allergic tests have been performed, in order to avoid any severe reaction to an eHF(Reference Kemp, Hill and Allen47, Reference Allen, Davidson and Day48).
In 2006, the Committee on Nutrition of the ESPGHAN recommended using eHF in cases of proven CMPA in infants and avoiding soya protein-based IF before the age of 6 months. Once the infant has reached the age of 6 months, if soya protein-based IF have been proposed because of their lower cost and greater acceptability, a test of clinical tolerance to soya protein should be performed first(Reference Agostoni, Axelsson and Goulet39). In 2008, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommended the use of eHF as a first choice in the case of proven CMPA and of AAF in the case of a failure of eHF(Reference Bhatia and Greer40).
Reimbursement of extensively hydrolysed formula and amino acid-based formula
The cost of formulae to be used during CMPA is as follows: AAF>milk eHF>rice eHF>soya protein formulae. Cows' milk- and rice-based eHf (where they are available) are usually sold in pharmacies. From a family point of view, the cost largely depends on the reimbursement rate by the health care system, with great variations from one country to another within the EU.
Introduction of complementary feeding in patients with cows' milk protein allergy
Milk-derived products and bovine meat
When the diagnosis of CMPA is made, the CMP elimination diet should be carefully explained to parents. It excludes not only milk, but also dairy products, cheese, butter, cream and all industrial products containing milk. The presence of CMP is normally mentioned on a product label in the following terms: cows' milk proteins; casein; caseinates; whey; lactalbumin; serum albumin. Within the EU, this labelling must be in compliance with the Directive 2003/89/EC amending Directive 2000/13/EC with regard to indication of the ingredients present in foodstuffs(49).
Children allergic to bovine serum albumin, i.e. 13–20 % of cases of CMPA, are generally allergic to beef and veal meat as well(Reference Martelli, De and Corvo50). The practice of excluding beef and veal is thus not systematically used in the treatment of CMPA. In the absence of diagnostic tests (skin tests or RAST), it is logical to avoid these meats during the diagnosis elimination diet and test their tolerance thereafter.
Lactose is not, in theory, contraindicated in the diets of children with CMPA. However, lactose used in the food industry may, depending on its degree of purification, contain significant traces of CMP, sometimes responsible for allergic reactions, which has led some authors to consider it to be inappropriate when used in food to be consumed by children with CMPA(Reference Niggemann, von Berg and Bollrath21). The reaction to CMP traces (up to 2 %) in ‘drug’ grade lactose is also possible(Reference Tsuruta, Sowa and Kobayashi51). Similarly, allergic individuals may react to CMP contaminants after the ingestion of probiotics raised on lactose or milk(Reference Moneret-Vautrin, Morisset and Cordebar52, Reference Bruni, Piacentini and Peroni53).
As IgE antibodies are directed primarily against conformational epitopes that are largely destroyed by heat, heat treatment might improve tolerance to milk and dairy products, as is observed with egg(Reference Konstantinou, Giavi and Kalobatsou54). In a recent survey, the majority (75 %) of a cohort of 100 allergic children, with a mean age of 7·5 years (range 2·1–17·3 years), tolerated products containing milk baked in the oven, i.e., in practice, cakes and pastries(Reference Nowak-Wegrzyn, Bloom and Sicherer55). The likelihood of such tolerance among younger children, and indeed for all cases of CMPA, is unknown. Moreover, in mice, pasteurisation of CMP seems to facilitate allergic sensitisation by enhancing the uptake of CMP by Peyer's patches(Reference Roth-Walter, Berin and Arnaboldi56).
Soya
After 6 months of age, and subject to prior verification of clinical tolerance, soya protein follow-on formulae and everyday soya foods can be used in complementary feeding. As stated above, such foods are tolerated by most children with CMPA.
Goats' and ewes' milk
Goats' and ewes' milk (fermented or not), cheeses and desserts provide a real benefit in terms of Ca intake, if tolerance to cows' milk has not been acquired after 1 year of age. However, goat's and ewe's milk proteins may cross-react with CMP in patients with CMPA, and the tolerance thereof will depend on individual susceptibility(Reference Carroccio, Cavataio and Iacono57).
Some studies have suggested the feasibility of recipes aimed at replacing IF based on cows' milk or soya, including the use of chicken or lamb as a protein source, with good results in terms of acceptability, tolerance and growth(Reference Jirapinyo, Densupsoontorn and Wongarn58, Reference Weisselberg, Dayal and Thompson59). Cantani(Reference Cantani60) also demonstrated the feasibility of an ‘oligo-antigenic’ diet (the so-called ‘Rezza diet’), based on meat, and which excludes the consumption of milk, egg, wheat or peanut products. Such diets have no place in countries where adequate substitutes are available.
Reading the labels and home-cooking
Access to product information from companies is regulated in the EU legislation (http://eur-lex.europa.eu/) by the Labelling Directive (Directive 2000/13/EC) and its later amendments that specifically refer to allergenic foods and require manufacturers to declare all ingredients, including milk or dairy products, present in pre-packaged foods sold in the EU. This directive has been amended several times with regard to allergens. The Directive 2003/89/EC introduced Annex IIIa, a list of allergenic foods that must always be labelled when present in a product and the Directive 2007/68/EC, which has the most recent amendment of Annex IIIa, lists all the allergenic foods that must be labelled as well as a few products derived from these foods for which allergen labelling is not required. The European Food Safety Authority website also provides information on food allergen labelling in Europe (http://www.efsa.europa.eu).
Milk-free products are more and more available in common retail outlets but still appear mostly in organic retail outlets, where parents usually get both the products and the dietary advice. A major issue for parents is the cooking of milk-free dishes, and their ability to use, in this preparation, the replacement formulae, based on their organoleptic properties and their ability to lend themselves to preparation of foods for infants.
Nutritional consequences of elimination diets
Nutritional risks
Elimination diets prevent the allergic inflammation induced by the offending food, but may have deleterious effects on the child's nutritional status and growth pattern. It is essential to monitor the elimination diet in order to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients. Undernutrition may be the consequence of an uncontrolled, inappropriate and/or excessively strict elimination diet(Reference Noimark and Cox2).
Nutritional risk is higher in the case of multiple food allergies: the elimination diet may easily result in deficiencies, especially if it includes multiple exclusions. Exclusion of foods such as egg and fish may cause a deficiency in n-3 long-chain PUFA(Reference Aldámiz-Echevarría, Bilbao and Andrade61). In a study conducted by Christie et al. (Reference Christie, Hine and Parker62), children with at least two food allergies were slightly shorter (height-for-age percentile) than those with a single food allergy (P < 0·05). Also, more than 25 % of children consumed less than two-thirds of the dietary reference intakes for Ca, vitamin D and vitamin E. The low Ca intake was especially marked in children with CMPA or multiple allergies.
The nutritional risks seem also to increase when CMPA is associated with asthma. Children suffering from a CMPA associated with asthma, for more than 4 years, and who were treated with corticosteroids, ingested only 25 % of the dietary reference intakes of Ca; accordingly, their height, bone mineral content, bone mineral density and bone age were below that of the reference population(Reference Jensen, Jørgensen and Rasmussen63).
Nutritional efficacy of substitute formulae
The ESPGHAN published in 2001 recommendations and comments on the nutritional and safety assessment of breast milk substitutes and other dietary products for infants for long- and short-term outcomes, and encouraged health care providers to promote the incorporation of these principles into their national regulatory processes(Reference Aggett, Agostoni and Goulet64). Only a few formulae marketed in Europe have been subject to studies evaluating adequately their nutritional efficacy (Nutramigen®, Pregestimil®, Neocate®, Nutramigen AA®, Blemil Arroz® (Ordesa, Barcelona, Spain), Althéra®).
Healthy infants fed with casein-based eHF (including Nutramigen®) had a poorer Fe status and an excessive amino acid intake, resulting in a rise in blood urea N and plasma amino acids, compared with infants fed with a standard formula, warranting both reducing and balancing the amino acid composition of some formulae(Reference Hernell and Lönnerdal65). In children with CMPA fed Althéra® for 6 months, length and head circumference were similar to Euro-growth standards, but weight was slightly lower, similarly to the comparator Neocate®(Reference Niggemann, von Berg and Bollrath21).
In Finnish children with proven CMPA, and fed from 7·5 months with a soya protein follow-on formula or with a soluble protein-based eHF (PeptidiTutteli®; Valio Limited, Helsinki, Finland), often supplemented with Ca and vitamin D, growth and nutritional status were adequate(Reference Seppo, Korpela and Lönnerdal66).
Infants (n 58) with confirmed CMPA-related atopic dermatitis were given openly either a rice-based eHF supplemented with lysine and threonine, a soya protein-based IF or a casein-based eHF and compared with an unrestricted diet in the absence of CMPA (n 30)(Reference Savino, Castagno and Monti67). The mean weight/age Z score at 2 years of age was similar in the three CMPA groups, but lower with the rice-based eHF diet than with the unrestricted diet during the periods between 9–12 months and 12–18 months, i.e. after the start of complementary feeding. Healthy infants fed for 16 weeks with a rice-based eHF diet supplemented with lysine and threonine (n 32) or with a cows' milk-based IF (n 33) had comparable normal growth and biochemical parameters(Reference Lasekan, Koo and Walters68). Infants breast fed for at least 4 months (n 93) and suffering from CMPA were either breast fed until 12 months of age or randomly weaned at 5–6 months of age to either a soya protein-based IF, a casein-based eHF or a rice-based eHF(Reference Agostoni, Fiocchi and Riva69). Weight/age and height/age Z scores were below the mean at 6 months of age in all groups, probably due to CMPA. With the rice-based eHF, the height/age Z score was identical to that of the soya group and the breast-fed group at 9 and 12 months. A rice-based eHF enriched with lysine, threonine and tryptophan was compared with a casein-based eHF in eighty-one infants with CMPA and a mean age of 4 months(Reference Reche, Pascual and Fiandor37). Infants with a baseline weight lower than average normalised their weight by 12 months of age using the rice-based eHF v. 18 months using the casein-based eHF. The growth pattern during breast-feeding or feeding with hydrolysates has been nicely investigated in the German Infant Nutritional Intervention (GINI) study(Reference Rzehak, Sausenthaler and Koletzko70): feeding with a casein-based eHF (Nutramigen®) induced a transient reduction in weight gain during the first year of life, without long-term consequences on BMI(Reference Rzehak, Sausenthaler and Koletzko71).
Several clinical trials have shown that Neocate® ensured normal growth in the case of an allergy to eHF and in the case of multiple food allergies, as well as a growth pattern identical to that obtained with eHF when they are well tolerated(Reference Hill, Murch and Rafferty32–Reference Niggemann, Binder and Dupont34). Another study has also shown that growth obtained with Nutramigen AA® in children presenting CMPA is comparable with that obtained with Nutramigen®, a casein-based eHF(Reference Burks, Jones and Berseth35).
The CNSFP regrets that all hydrolysates available on the European market have not been subject to a detailed assessment of their nutritional efficacy, in accordance with the regulations.
Addition of compounds presumed to be active on the allergy
The use of compounds presumed to be active on the immuno-allergic reaction, in addition to the milk substitute, should be considered with great caution in the current state of evidence. The putative interest of some probiotics has been suggested, but there is currently no evidence that probiotics can be helpful in the treatment of a child with CMPA(Reference Floch, Walker and Guandalini72). A recent study has argued against the efficacy of probiotics (Lactobacillus casei and Bifidobacterium lactis Bb CRL431-12) in the process of tolerance acquisition(Reference Hol, van Leer and Elink Schuurman73). There is no study demonstrating the effectiveness of long-chain-PUFA in the treatment of CMPA.
Duration of the elimination diet
Variable duration and frequent incomplete recovery from a cows' milk protein allergy
It can take as long as between 2 and 4 weeks for the symptoms of an infant who suffers from a CMPA to disappear, when following an elimination diet(Reference Vandenplas, Koletzko and Isolauri8). The evolution of the CMPA when treated with an elimination diet is usually towards spontaneous remission, more or less in parallel with the evolution of biological tests, albeit that it is sometimes slow and incomplete(Reference Høst and Halken74–Reference Iacono, Cavataio and Montalto76). According to Høst et al. (Reference Høst, Halken and Jacobsen77), remission rates are 45–50 % at 1 year, 60–75 % at 2 years and 85–90 % at 3 years (with an associated food allergy in 50 % of the cases). In the study by Carroccio et al. (Reference Carroccio, Cavataio and Montalto78), remission rates are lower, at 30, 54·5 and 70 % at 1, 2 and 3 years, respectively. Persistent cases of CMPA are characterised by (1) the intensity of the familial atopic disease, (2) a longer period between the consumption of the CMP and the onset of symptoms, (3) a high frequency of multiple food allergy and allergic diseases(Reference Iacono, Cavataio and Montalto76) and (4) an allergy to casein more than to soluble proteins.
CMPA with early gastrointestinal symptoms has a better prognosis(Reference de Boissieu and Dupont33). CMPA with IgE-mediated symptoms is associated with an increased risk of persistence, development of reactions to other foods and the occurrence of asthma and rhino-conjunctivitis later in childhood(Reference Høst, Halken and Jacobsen77, Reference Carroccio, Cavataio and Montalto78). In a study by Saarinen et al. (Reference Saarinen, Pelkonen and Mäkelä79), 15 % of children with IgE-mediated CMPA had persistent symptoms after the age of 8·6 years, while patients with non-IgE-mediated CMPA were all free of disease by the age of 5 years. In another study by Skripak et al. (Reference Skripak, Matsui and Mudd80), spontaneous resolution of IgE-mediated CMPA occurred in 19 % of children at 4 years, 42 % at 8 years and 79 % at 16 years. Patients with persistent allergy had the highest levels of specific IgE. The coexistence of asthma and allergic rhinitis is a factor that presents a poor prognosis.
It is common for a CMPA to be resolved, but this resolution is not always complete. According to Kokkonen et al. (Reference Kokkonen, Tikkanen and Savilahti81), some children considered to be free of CMPA may retain a ‘residual disease’ and may not be able to tolerate a ‘normal’ intake of milk and dairy products. At the age of 10 years, 45 % of children, who were reliably diagnosed with a CMPA during the first year of life and who have since been considered free of that CMPA, complained of gastrointestinal symptoms (diarrhoea, abdominal pain and/or nausea) in relation to the ingestion of dairy products, v. 10 % in the control group. The prevalence of lactose intolerance during the hydrogen breath test was 14 % in CMPA children, v. 3 % in the control group. In addition, ‘incomplete recovery’ encompasses cases where the loss of symptoms is accompanied by persistent sensitisation, which may explain some intriguing issues such as recurrence of symptoms during intercurrent illnesses or during pregnancy and lactation. Noticeably, these situations may be encountered in parents of children being taken care of with CMPA, albeit with no studied frequency at the moment.
The required duration of the strict elimination diet cannot be clearly established a priori for a given individual. In practice, however, an early case of CMPA that is non-IgE-dependent, and which presents with predominantly digestive manifestations, may only last for a short period of time, and may warrant a review with further tests at the age of 9 months(Reference de Boissieu and Dupont33). However, where there is a later onset of CMPA, which is IgE-dependent, and which presents with skin manifestations among others, there is the possibility that this type of allergy could last longer and should not require further evaluation before the age of 1 year(Reference Saarinen, Pelkonen and Mäkelä79, Reference Skripak, Matsui and Mudd80).
Milk, oral food challenge and the adaptation of the duration and nature of the elimination diet for the individual
A decision on whether to discontinue the elimination diet should be made with reference to an oral food challenge (OFC) or provocation test on cows' milk, which should be performed in the hospital day care unit, and followed by the gradual reintroduction of milk and dairy products at home. The protocol for such reintroduction should be discussed, particularly where a severe reaction is anticipated(Reference Høst, Andrae and Charkin82–Reference Lieberman85). IgE-mediated CMPA carries the risk of an anaphylactic shock to milk. Some cases of non-IgE-mediated CMPA, such as enterocolitis induced by food proteins, carry the risk of dehydration from diarrhoea and vomiting within 5–6 h after the start of the test, which may require parenteral rehydration(Reference Nowak-Wegrzyn and Muraro86).
According to a group of international experts, ‘the test must be carried out in a hospital in an area equipped for severe reactions, close to an intensive care unit, by a medical personnel and paramedics used to carry out these tests(Reference Rancé, Deschildre and Villard-Truc87). Information to patients and their families and informed consent are essential. The physician must be present on site and nurses must be experienced and able to detect adverse reactions. A day of hospitalisation is usually sufficient. However, monitoring during at least 4 h after administration of the last dose is recommended to cover the period of severe and immediate reactions and allow the diagnosis of delayed reactions. The occurrence of a reaction can lead to a conventional hospitalisation for observation. For delayed symptoms such as eczema, the OFC can start in a hospital setting but may be continued outside the hospital after returning home’. The CNSFP adds the following comments: most children with non-IgE-mediated CMPA do not need day-care admission, since they are not at risk of anaphylactic shock. Some of them, however, exhibit a food protein-induced enteropathy syndrome, a non-IgE-mediated disorder, which puts them at risk of dehydration during the 4 h following the end of the OFC. If a child had an inadvertent milk challenge (e.g. a glass of milk at a friend's house) and it is clear from the medical history that no reaction occurred, admitting the child to hospital for a similar challenge does not seem worthwhile.
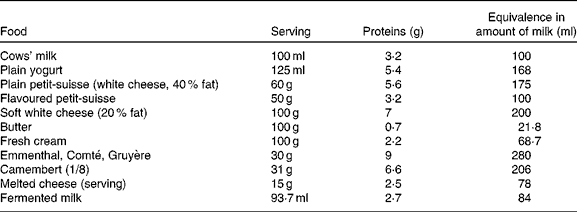
Following the OFC, the progressive reintroduction of CMP continues at home. The clinical response to CMP may occur up to 1 month after the commencement of the OFC(Reference Carroccio, Cavataio and Montalto78). This progressive reintroduction at home allows determining the CMP dose that the child is able to tolerate. This dose may correspond to the usual intake of milk and dairy products in a Western diet or be more limited in children who continue to suffer from the ‘residual disease’(Reference Kokkonen, Tikkanen and Savilahti81). The current state of the research does not allow to say what proportion of children whose OFC has demonstrated the consumption of a quantity of milk equivalent to one bottle, without difficulty, will retain a limited long-term tolerance to dairy products. The persistence of clinical symptoms suggestive of the recurrence of a CMPA during the gradual increase of CMP intake at home does not ipso facto warrant a return to the strict exclusion of CMP. Indeed, several recent studies have indicated that the continued presence of CMP in the diet at a tolerated dose facilitates the acquisition of a long-term tolerance(Reference Allen, Campbell and Kemp88, Reference Barbi, Berti and Longo89). The increase in food diversity allowed into the diet also makes social life easier. Such management requires a full education and the active participation of parents, and is not always feasible. It is facilitated by the knowledge of the protein concentrations in the dairy products available (Table 4).
Table 4 Milk protein content of different dairy products and their equivalence (for proteins) in terms of cows' milk amount
In conclusion, although the spontaneous resolution of CMPA is common, it is not always complete, as children often spontaneously limit their intake of milk products to the tolerated dose, i.e. the dose for which ingestion does not trigger symptoms. The regular encounter with the allergen at a low dosage could facilitate the acquisition of a tolerance towards the allergen. Once tolerance is attained, the regular intake of the allergen is necessary in order to maintain that tolerance.
Progressive normalisation of diet: difficulties in acceptability
The prevalence of food neophobia, i.e. the refusal by children to eat new food, known to be a normal phenomenon between 2 and 10 years of age, seems to be more common or pronounced when an elimination diet has been imposed by a food allergy. An evaluation using a standardised scale of food neophobia and a familiar food questionnaire showed that children with a personal history of allergy (mean age 7 years, 2 months) were more reluctant to try new foods than their non-allergic sibling (average age 9 years, 5 months)(Reference Rigal, Reiter and Morice90). Several factors may increase neophobia: the severity of the symptoms, the duration of the delay in diagnosis, the difficulty of the elimination diet and the monotony of meals.
Tolerance induction and immunotherapy (in specialised units)
The induction of tolerance aims at ‘forcing’ a lack of tolerance of CMP, starting with very low doses, increased very gradually to induce ‘desensitisation’(Reference Niggemann, Staden and Rolinck-Werninghaus91). The term ‘immunotherapy’ is probably more appropriate: immunotherapy leads to either a ‘tolerance’, the final state of non-reactivity to the allergen independent of its regular use, whereas ‘desensitisation’ simply increases the threshold of reactivity. The technique of Meglio et al. (Reference Meglio, Bartone and Plantamura92), studied in twenty-one children with IgE-mediated CMPA persisting beyond the age of 5 years, i.e. with a low chance of spontaneous recovery, consisted of administering a very low initial dose of milk (a drop of milk diluted to 1/25th), which was subsequently doubled every 7 d. After 6 months, fifteen children tolerated a daily dose of 200 ml of milk, three a dose between 40 and 80 ml and three retained allergic reactions even to small doses. In a randomised study of this ‘oral tolerance’ protocol in ninety-seven children over 5 years of age and suffering from severe CMPA, 36 % of treated children achieved complete tolerance after 1 year, 54 % became partially tolerant (5–150 ml milk/d) and 10 % did not complete the protocol because of respiratory or gastrointestinal manifestations, while none of the children became tolerant in the control group(Reference Longo, Barbi and Berti93). A protocol of ‘oral tolerance’ in thirty children, who suffered from a CMPA and had an average age of 8 years, allowed 23 % of children to tolerate a normal diet after 1 year, 13 % to tolerate a milk intake ≥ 150 ml/d and 54 % to exhibit a partial tolerance, while 10 % dropped out of the protocol for adverse effects, and no improvement was observed in thirty untreated controls(Reference Mazer94). The maintenance of a tolerance requires the body to be regularly exposed to the allergen, as is confirmed by other studies(Reference Rolinck-Werninghaus, Staden and Mehl95). This technique has the major advantage of substantially reducing the risk of severe reactions after accidental ingestion of the allergen(Reference Staden, Rolinck-Werninghaus and Brewe96).
Sublingual desensitisation is a technique used in the realm of respiratory allergies and can be adapted to be used in the assessment of food allergies. A study of this type, on patients with persistent CMPA, was carried out using half-skimmed milk placed under the tongue every day for 2 min before breakfast, at an initial dose of 0·1 ml, increased by 0·1 ml every 15 d, and reaching a dose of 1 ml. The OFC showed an increase in the milk dose inducing a reaction after 6 months, and the diet could be normalised in 50 % of patients(Reference de Boissieu and Dupont97). This technique appears to reduce the risk of accidental allergic reactions to small amounts of milk or even to cure some children; it is simple to perform and without serious adverse effects, but its benefit must be confirmed in randomised studies to determine the amount of milk to use and the time required to optimise the results.
It is also possible to envisage the use of a patch as a desensitisation technique, and an initial study has analysed its safety, tolerance and potential benefits(Reference Dupont, Kalach and Soulaines98).
Management by parents and at school
Parental information
Providing information to parents at the different stages of the disease management is crucial, especially to facilitate the dialogue with the various settings that accommodate the allergic child, such as the school(Reference Hu, Grbich and Kemp99). A Swedish study has reported a method of group therapeutic education in a paediatric health centre(Reference Mikkelsen, Lissner and Borres100). It must be emphasised that the initiation of an elimination diet, which is consistent with the recognition of a risk resulting from the accidental ingestion of dairy products, must be accompanied by a thoughtful consideration of the conditions of implementation of treatment with epinephrine in situations of a possible anaphylactic shock or acute laryngeal oedema. The modalities of implementing such constraints are now facilitated by self-injection pens, the use of which can be considered in the scenarios published in 2005(Reference Sicherer and Simons101).
Management at school
Children with CMPA should be able to attend school and follow their educational curriculum or be accommodated in the community while adhering to their elimination diet. In practice, the school doctor's mission is to establish a ‘contract’ between the family, on the one hand, and the school authorities (the educational team, the authorities responsible for school lunches), on the other hand.
Recommendations and statements
In the current state of knowledge, and based on the analysis of the literature presented in the present review, the CNFSP makes the following recommendations and statements, which are briefly summarised in Fig. 1.
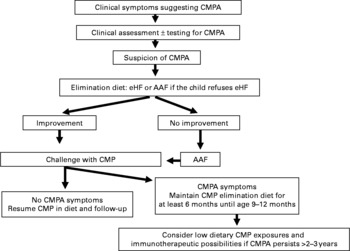
Fig. 1 Decision tree summarising the recommendations of the Nutrition Committee of the French Society of Paediatrics. CMP, cows' milk protein; CMPA, CMP allergy; eHF, extensively hydrolysed formula; AAF, amino acid-based formula.
Diagnosis of cows' milk protein allergy
The diagnosis of CMPA requires first the suspicion of diagnosis based on symptoms described in the medical history, and, second, the elimination of CMP from the infant's diet. Without such rigorous analysis, the elimination of CMP is unjustified, and sometimes harmful.
Dietary management of cows' milk protein allergy
1 If an infant displays clinical symptoms of CMPA during exclusive breast-feeding, the mother should continue to breast feed, while eliminating from her own diet all foods containing CMP, which must lead to the rapid disappearance of symptoms in the infant within 2–3 weeks. When the symptoms have been resolved, the progressive reintroduction of CMP into the mother's diet will allow the infant's tolerance levels to be tested.
2 If clinical symptoms occur during weaning, the best option is to resume exclusive breast-feeding (without any elimination diet in the mother).
3 If the infant is not breast fed or if the mother cannot or no longer wishes to breast feed, the first choice is an extensive hydrolysate (eHF) of CMP.
4 If the eHF fails to achieve the desired result, an AAF is warranted.
5 To date, very few products (Nutramigen®, Pregestimil®, Neocate®, Nutramigen AA®, Blemil Arroz®, Althéra®) have been shown efficient, both in terms of allergy and growth.
6 In the case of anaphylaxis, eosinophilic oesogastroenteropathy, failure to thrive or severe colitis, the use in the first intention of either an eHF or an AAF is a valid option.
7 Rice protein-based eHF offer an alternative to eHF from animal origin.
8 Soya protein IF can be used after the age of 6 months, after ensuring a good clinical tolerance to soya.
9 The diet must be carefully explained to parents, which includes education about how to read labels. The initial help of a dietitian seems essential.
10 In terms of meat, both beef and veal are tolerated by the majority of children with CMPA.
11 Some products (e.g. medicines for oral use) may contain CMP.
12 Compliance with dietary recommendations, their tolerance and efficacy (disappearance of symptoms and adequate growth) should be regularly assessed.
13 The use of supplements may be required (e.g. for Fe, Ca and vitamin D) during an elimination diet.
Relaxation of the management of CMPA
1 Spontaneous remission of CMPA is the most common outcome during the first 2 to 3 years.
2 The age of recovery varies depending on the child and the type of CMPA, whether it is IgE-mediated or not, with the former being more persistent.
3 Once the child reaches the age of 9–12 months, an OFC is carried out in the hospital ward to assess the development of tolerance and, if possible, to allow for the continued reintroduction of CMP at home.
4 If necessary, repeated OFC allow avoiding the unnecessary prolongation of the elimination diet.
5 The spontaneous recovery from CMPA is not always a complete recovery, and the daily dose of milk/dairy products tolerated by the child may be limited. The current therapeutic options are designed to accelerate the acquisition of tolerance thereof, which seems to be facilitated by repeated exposure to CMP.
Summary of issues and future needs
1 The cost and reimbursement by the health care system of cows' milk and rice protein-based eHF, AAF, and soya protein-based IF varies from one member-state to another one in the EU. This is very likely to have a strong influence in the management of CMPA, especially in the choice of substitute formulae.
2 Research and regulatory needs. Efforts should be made by governments to help families afford the cost of the disease. Products should be marketed following appropriate testing, analysing both their hypoallergenicity and their adaptation to the clinical situation, such as the role of AAF in allergy to hydrolysates.
Acknowledgements
This review received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors. The authors had no personal, commercial, political or academic conflicts of interest. Financial conflicts of interest (research funding, payment for lectures or travel, consultancies or company support for staff) are reported by C. D. (Danone, Nestlé, Novalac, Sodilac), J. P. C. (Danone, Mead-Johnson, Nestlé, Sodilac), D. d. B. (Danone, Mead-Johnson), A. B. (Danone, Nestlé, Novalac, Sodilac), J. L. B. (Syndifrais), D. D. (Nestlé), R. H. (Danone), J. G. (Danone), J. P. G. (Danone, Mead-Johnson, Sodilac), O. G. (Danone, Mead-Johnson), M. V. (Danone) and D. T. (Danone, Mead-Johnson, Nestlé). A. B., M. L. F. and D. R. declare that they have no conflicts of interest. The contribution made by each author was as follows: C. D. was the main contributor; J. P. C., D. d. B., M. V. and D. T. were responsible for additional writing and reviewing of the manuscript; A. B., J. L. B., A. B., D. D., M. L. F., J. G., J. P. G., O. G., R. H. and D. R. were involved in the reviewing of the manuscript.







