Ecandrewsite, the zinc analogue of ilmenite, is a new mineral which was first described from the Broken Hill lode in 1970 and discovered subsequently in ores from Little Broken Hill (New South Wales) and the San Valentin Mine, Spain. The name ‘ecandrewsite’ was used in a partial description of the mineral in ‘Minerals of Broken Hill’ (1982), thereby establishing the Little Broken Hill locality, specifically the Melbourne Rockwell Mine, as the type locality. Microprobe analysis of ecandrewsite from the type locality gave ZnO 30.42 (wt.%), FeO (total Fe) 11.37, MnO 7.64, TiO2 50.12, total 99.6%, yielding an empirical formula of (Zn0.59Fe0.24Mn0.17)1.00Ti0.99O3 based on 3 oxygen atoms. All compositions from Little Broken Hill and the San Valentin Mine are ferroan manganoan ecandrewsite. The strongest lines in the X-ray powder diffraction data are (d in Å, (hkil), I/Io):2.746, (10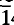 4), 100; 2.545, (11
4), 100; 2.545, (11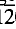 0), 80; 1.867, (02
0), 80; 1.867, (02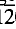 4), 40; 3.734, (01
4), 40; 3.734, (01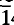 2), 30; 1.470, (3030), 30; 1.723, (11
2), 30; 1.470, (3030), 30; 1.723, (11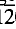 6), 25. Ecandrewsite is hexagonal, space group RR3¯ assigned from a structural study, with a = 5.090(1), c = 14.036(2)Å, V = 314.6(3)Å3, Z = 6, D(calc.) = 4.99. The mineral is opaque, dark brown to black with a similar streak, and a submetallic lustre. In plane polarized light the reflection colour is greyish white with a pinkish tinge. Reflection pleochroism is weak, but anisotropism is strong with colours from greenish grey to dark brownish grey. Reflectance data in air between 470 and 650 nm are given. At the type locality, ecandrewsite forms disseminated tabular euhedral grains up to 250 × 50 µm, in quartz-rich metasediments. Associated minerals include almandine-spessartine, ferroan gahnite and rutile. The name is for E. C. Andrews, pioneering geologist in the Broken Hill region of New South Wales. Type material consisting of one grain is preserved in the Museum of Victoria (M35700). The mineral and name were approved by the IMA Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names in 1979.
6), 25. Ecandrewsite is hexagonal, space group RR3¯ assigned from a structural study, with a = 5.090(1), c = 14.036(2)Å, V = 314.6(3)Å3, Z = 6, D(calc.) = 4.99. The mineral is opaque, dark brown to black with a similar streak, and a submetallic lustre. In plane polarized light the reflection colour is greyish white with a pinkish tinge. Reflection pleochroism is weak, but anisotropism is strong with colours from greenish grey to dark brownish grey. Reflectance data in air between 470 and 650 nm are given. At the type locality, ecandrewsite forms disseminated tabular euhedral grains up to 250 × 50 µm, in quartz-rich metasediments. Associated minerals include almandine-spessartine, ferroan gahnite and rutile. The name is for E. C. Andrews, pioneering geologist in the Broken Hill region of New South Wales. Type material consisting of one grain is preserved in the Museum of Victoria (M35700). The mineral and name were approved by the IMA Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names in 1979.

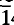 4), 100; 2.545, (11
4), 100; 2.545, (11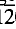 0), 80; 1.867, (02
0), 80; 1.867, (02