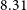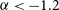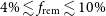48 results
Effects of Siderophores on Pb and Cd Adsorption to Kaolinite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 53 / Issue 6 / December 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 557-563
-
- Article
- Export citation
Habitat heterogeneity supports day-flying Lepidoptera in oil palm plantations
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Tropical Ecology / Volume 39 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation

The Many Faces of Creativity
- Exploring Synaesthesia through a Metaphorical Lens
-
- Published online:
- 25 January 2023
- Print publication:
- 09 February 2023
-
- Element
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Aerobic exercise enhances cognitive training effects in first-episode schizophrenia: randomized clinical trial demonstrates cognitive and functional gains
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 10 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 August 2022, pp. 4751-4761
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Factors associated with breast-feeding initiation and continuation in Canadian-born and non-Canadian-born women: a multi-centre study
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 25 / Issue 10 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 December 2021, pp. 2822-2833
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Thin ice, deep snow and surface flooding in Kotzebue Sound: landfast ice mass balance during two anomalously warm winters and implications for marine mammals and subsistence hunting
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 67 / Issue 266 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2021, pp. 1013-1027
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
University students and staff able to maintain low daily contact numbers during various COVID-19 guideline periods
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2021, e169
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Two - Street Vendor Struggles: Maintaining a Livelihood Through the COVID-19 Lockdown in Hanoi, Vietnam
-
-
- Book:
- Volume 1: Community and Society
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 13 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 22 July 2021, pp 21-30
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Comparison of metrics used to track central-line–associated bloodstream infections (CLABSIs) and catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) across a regional network
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 11 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2021, pp. 1712-1714
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
5 - Multimodality
-
-
- Book:
- Analysing Religious Discourse
- Published online:
- 18 June 2021
- Print publication:
- 08 July 2021, pp 70-90
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
In pursuit of the holy grail: Improving C. difficile testing appropriateness with iterative electronic health record clinical decision support and targeted test restriction
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 7 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2021, pp. 840-847
- Print publication:
- July 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Profiling Social Cognition in Premanifest Huntington's Disease
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 28 / Issue 3 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 May 2021, pp. 217-229
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sunken ships and screaming banshees: metaphor and evaluation in film reviews
-
- Journal:
- English Language & Linguistics / Volume 26 / Issue 1 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 April 2021, pp. 75-103
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sustained reduction in catheter-associated urinary tract infections using multi-faceted strategies led by champions: A quality improvement initiative
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 7 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2021, pp. 925-929
- Print publication:
- July 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Remnant radio galaxies discovered in a multi-frequency survey
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2021, e008
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effective Communication Following Pregnancy Loss: A Study in England
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Quarterly of Healthcare Ethics / Volume 30 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 December 2020, pp. 175-187
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Developing a New Conceptual Framework of Meaningful Interaction for Understanding Social Isolation and Loneliness
-
- Journal:
- Social Policy and Society / Volume 21 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2020, pp. 172-193
- Print publication:
- April 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Efficacy of the Zero Suicide framework in reducing recurrent suicide attempts: cross-sectional and time-to-recurrent-event analyses
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 219 / Issue 2 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 November 2020, pp. 427-436
- Print publication:
- August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comparison of Metrics Used to Track CLABSIs and CAUTIs Across a Regional Network
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 41 / Issue S1 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2020, pp. s178-s179
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Structured Psychological Support for people with personality disorder: feasibility randomised controlled trial of a low-intensity intervention
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 6 / Issue 2 / March 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 March 2020, e25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation