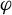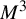30 results
Overcoming major barriers in seed ecology research in developing countries
-
- Journal:
- Seed Science Research / Volume 33 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 January 2024, pp. 172-181
-
- Article
- Export citation
Selected rock powders as sources of nutrients for soil fertilization and maize-wheat grain production in southern Brazil
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 161 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 December 2023, pp. 654-668
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cancellations of periodic orbits for non-singular Morse–Smale flows
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 44 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 May 2023, pp. 1123-1171
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Covering action on Conley index theory
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 43 / Issue 5 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2022, pp. 1633-1665
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Maternal antenatal depression and child mental health: Moderation by genomic risk for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 32 / Issue 5 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2021, pp. 1810-1821
-
- Article
- Export citation
The early care environment and DNA methylome variation in childhood
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 30 / Issue 3 / August 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2018, pp. 891-903
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Incidence and risk factors for Dengue virus (DENV) infection in the first 2 years of life in a Brazilian prospective birth cohort
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 145 / Issue 14 / October 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2017, pp. 2971-2979
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Limpograss (Hemarthria altissima) Tolerance to Hexazinone
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 31 / Issue 5 / October 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2017, pp. 682-688
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tillering dynamics of Mulato grass subjected to strategies of rotational grazing management
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 155 / Issue 7 / September 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2017, pp. 1082-1092
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evaluation Of Tooth Enamel Content Exposed To Bleaching Gel
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 21 / Issue S6 / August 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 September 2015, pp. 60-61
- Print publication:
- August 2015
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A global two-dimensional version of Smale’s cancellation theorem via spectral sequences
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 36 / Issue 6 / September 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2015, pp. 1795-1838
- Print publication:
- September 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
High sodium intake during postnatal phases induces an increase in arterial blood pressure in adult rats
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 112 / Issue 12 / 28 December 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2014, pp. 1923-1932
- Print publication:
- 28 December 2014
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Interactions of Plasmodium juxtanucleare and chicken anaemia virus: establishing a model
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 140 / Issue 14 / December 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2013, pp. 1777-1788
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mechanisms of cisplatin ototoxicity: theoretical review
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 127 / Issue 6 / June 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 May 2013, pp. 536-541
- Print publication:
- June 2013
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Brazilian AMS Radiocarbon Laboratory (LAC-UFF) and the Intercomparison of Results with CENA and UGAMS
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 55 / Issue 2 / 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2016, pp. 325-330
- Print publication:
- 2013
-
- Article
- Export citation
Treatment with Selemax®, a selenium-enriched yeast, ameliorates experimental arthritis in rats and mice
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 108 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2012, pp. 1829-1838
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation