166 results
4 Methamphetamine, cannabis, HIV, and their combined effects on neurocognition
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 797-798
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Cannabis use may attenuate neurocognitive performance deficits resulting from methamphetamine use disorder
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 30 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2023, pp. 84-93
-
- Article
- Export citation
Emotional health and its association with neurocognition in Hispanic and non-Hispanic White people with HIV
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 30 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 April 2023, pp. 56-66
-
- Article
- Export citation
14 - In the Undergrowth: Llwyn a Pherth and Sexual Deviancy in Medieval Wales
-
-
- Book:
- Women's Literary Cultures in the Global Middle Ages
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 09 January 2024
- Print publication:
- 04 April 2023, pp 261-276
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Cannabis use and psychotic disorders in diverse settings in the Global South: findings from INTREPID II
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 15 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2023, pp. 7062-7069
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Urbanicity and rates of untreated psychotic disorders in three diverse settings in the Global South
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 14 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 January 2023, pp. 6459-6467
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Life events and psychosis: case–control study from India, Nigeria, and Trinidad and Tobago
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 8 / Issue 5 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2022, e168
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
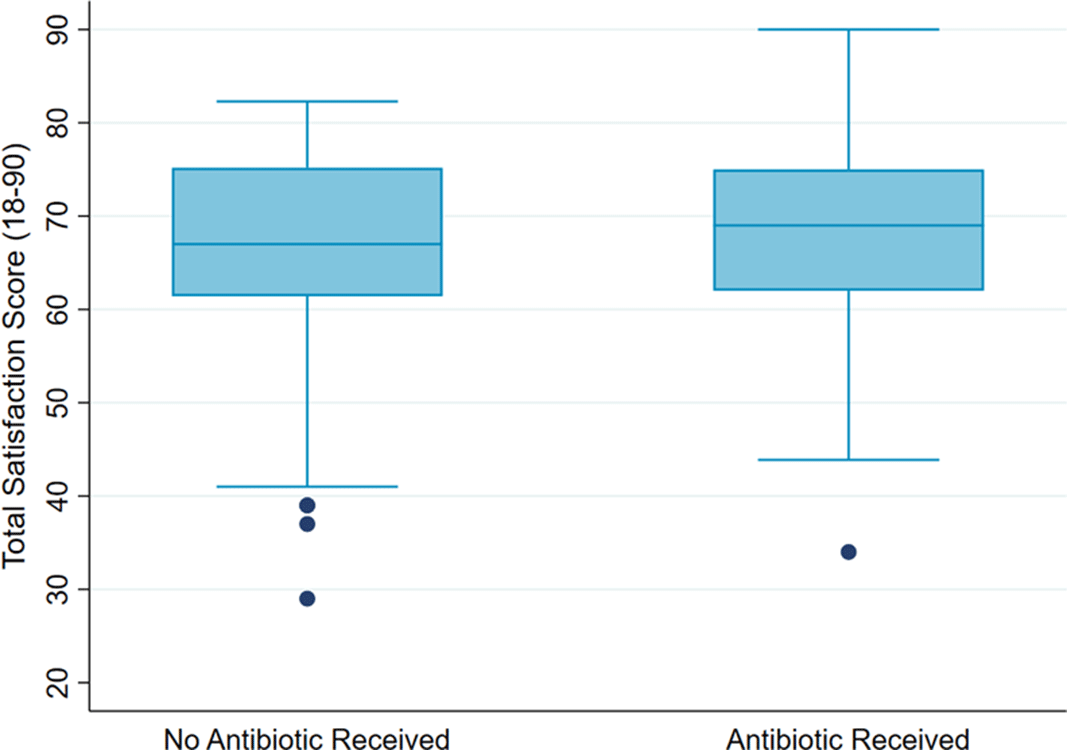
Association of antibiotics with veteran visit satisfaction and antibiotic expectations for upper respiratory tract infections
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 2 / Issue 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2022, e100
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Veteran Satisfaction for Upper Respiratory-Tract Infection (URI) Visits Is Not Associated with Antibiotic Receipt But Is Associated with Antibiotic Expectation
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 1 / Issue S1 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2021, p. s33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Daily Cannabis Use is Associated With Lower CNS Inflammation in People With HIV
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 27 / Issue 6 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 July 2021, pp. 661-672
-
- Article
- Export citation
Simulation and flow physics of a shocked and reshocked high-energy-density mixing layer
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 915 / 25 May 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2021, A84
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chapter 23 - Criminogenic Risk and Mental Health: A Complicated Relationship
- from Part IV - Nonpsychopharmacological Treatment Considerations
-
-
- Book:
- Decriminalizing Mental Illness
- Published online:
- 19 October 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 January 2021, pp 241-250
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 22 - Examining Violence Among Not Guilty by Reason of Insanity State Hospital Inpatients Across Multiple Time Points: The Roles of Criminogenic Risk Factors and Psychiatric Symptoms
- from Part IV - Nonpsychopharmacological Treatment Considerations
-
-
- Book:
- Decriminalizing Mental Illness
- Published online:
- 19 October 2021
- Print publication:
- 07 January 2021, pp 231-240
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
The Qualitative Transparency Deliberations: Insights and Implications
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics / Volume 19 / Issue 1 / March 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2021, pp. 171-208
- Print publication:
- March 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Placental adaptations in a nonhuman primate model of gestational protein restriction
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 12 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2020, pp. 908-914
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Recreating the OSIRIS-REx slingshot manoeuvre from a network of ground-based sensors
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 November 2020, e049
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Guide for Caring for Patients Amidst the Novel Coronavirus Pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 15 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2020, p. e19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A theory limited in scope and evidence
-
- Journal:
- Behavioral and Brain Sciences / Volume 43 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2020, e171
-
- Article
- Export citation
How do ethnicity and deprivation impact on life expectancy at birth in people with serious mental illness? Observational study in the UK
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 51 / Issue 15 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 May 2020, pp. 2581-2589
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
23 - Implications of the Changing Nature of Work for Employee Health and Safety
- from Part III - Implications for Talent Management and Impact on Employees
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of the Changing Nature of Work
- Published online:
- 02 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 23 April 2020, pp 489-508
-
- Chapter
- Export citation